Demystifying Multiplexing Technologies:WDM, TDM and SDM
What is multiplexing Technologies?
In optical fiber communication, multiplexing is considered the primary means for expanding existing fiber network infrastructure. It allows multiple independent signals to be transmitted over the same communication channel, thereby improving channel utilization. In multiplexing, multiple signals share the same transmission medium, effectively utilizing different parameters or dimensions to enable these signals to be transmitted in the same time or space without interfering with each other.
The most commonly used multiplexing technologies at present include wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), time division multiplexing (TDM), frequency division multiplexing (FDM), and code division multiplexing (CDM). The following will focus on the in-depth introduction of these technologies.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
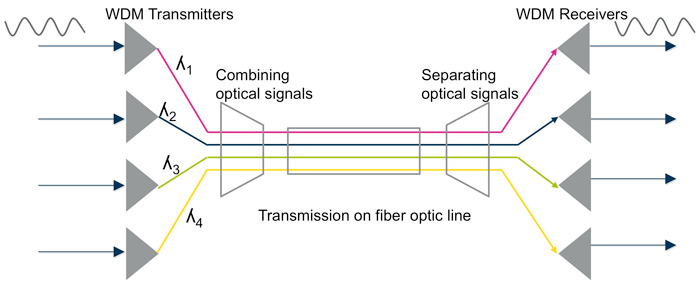
WDM is one of the optical multiplexing techniques that increases bandwidth by multiplexing a variety of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths. Each signal at WDM wavelengths is independent of any protocol and any speed. WDM technology allows bidirectional communications simultaneously over a single optical fiber. The foundation of WDM simplifies the network to a single virtual optical fiber network instead of using multiple forms of signals with different fibers and services. In this way, WDM increases the bandwidth and lowers the networking cost by reducing the needed fibers.
There are two different wavelength patterns of WDM system, coarse wave division multiplexing (CWDM) and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM). CWDM and DWDM are based on the same concept of using multiple light wavelengths on a single fiber, but differ in the spacing of the wavelengths, numbers of channels, and the ability to amplify the multiplexed signals in the optical space. In a WDM system, different optical signals are combined (multiplexed) together at one end of the optical fiber and separated (demultiplexed) into different channels at the other end.
If you want to know more, check out WDM Basics: Understanding Wavelength Division Multiplexing Technology.
Time Division Multiplexing
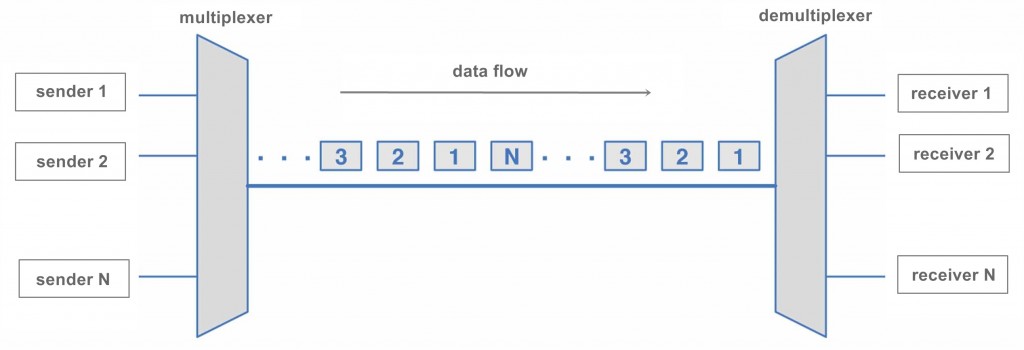
TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) is a technique that divides different signals into time slots and then transmits them in the order of these slots. In optical communication, Optical Time-Division Multiplexing (OTDM) is a variant of TDM that utilizes the time resolution of optical pulses for time-division multiplexing of optical signals.
Specifically, OTDM multiplexes several low-bit-rate optical channels into a fixed electrical clock period, thereby increasing the transmission speed. Each signal is transmitted by dividing the time frame into time slots, with each slot dedicated to a message signal. Based on time, each low-speed channel is allocated to a specific position, operating in synchronized mode. Therefore, OTDM achieves multiplexing of multiple signals by temporally segmenting and interleaving different optical channels.
Usually, the optical pulse width is shortened in order to multiplex more channels within the fixed clock period. In addition, the shortened pulse width can reduce the crosstalk between channels because of more room left in bit rate. However, short pulse width results in heavy dispersion as traveling distance increases. Therefore, transform-limited pulse and dispersion slope compensation technique need to be used to reduce the dispersion effect on OTDM.
Space Division Multiplexing
SDM(Space Division Multiplexing) is a technology that utilizes the spatial dimension to simultaneously deliver different data streams by creating parallel spatial channels. This technology is commonly used in multi-input multi-output (MIMO) system. MIMO incorporates at least two antennas at the transmitter side and at least two antennas at the receiver side. And MIMO signal processing is already widely used in current coherent optical transmission systems with polarization division multiplexing (PDM) over standard single-mode fibers. It is believed that by adopting strategies using multi-core and mutil-mode fibers, long-haul transmission distance and high-speed data rates with high-density SDM are possible to achieve.
The emergence of space division multiplexing technology provides a new development direction for the capacity improvement of optical cable transmission systems. In recent years, people have continued to study its inclusion in submarine optical cables to expand transmission capacity. Please check Application of Space Division Multiplexing (SDM) in Submarine Optical Cable for details.
Conclusion
In summary, this article has introduced three commonly used multiplexing technologies in the field of optical communication – Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM), Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), and Space Division Multiplexing (SDM). These technologies play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of efficient data transmission.
Among all the multiplexing technologies, WDM finds the most extensive application in optical communication. As different multiplexing techniques have their limitations in some aspects, it is usually suggested to use more than one technique in fiber optic networks to get the best transmission performance.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023














