The Advantages and Disadvantages of Optical Fiber
Optical fiber is rising in both telecommunication and data communication due to its unsurpassed advantages: faster speed with less attenuation, less impervious to electromagnetic interference (EMI), smaller size and greater information carrying capacity. The unceasing bandwidth needs, on the other hand, are also yielding significant growth in optical fiber demands. Let’s take a review of common fiber optic cable types, explore the advantages and disadvantage of optical fiber, and learn tips on selecting fiber optic cable.
What Is Optical Fiber?
Optical fiber uses light pulses instead of electrical pulses to transmit information, thus delivers hundreds of times higher bandwidth than traditional electrical systems. Fiber optic cable can be protected by sheathing and armor to make it resistant to harsh environmental conditions. Hence it is widely adopted in commercial business, governments, military and many other industries for voice, video and data transmission.
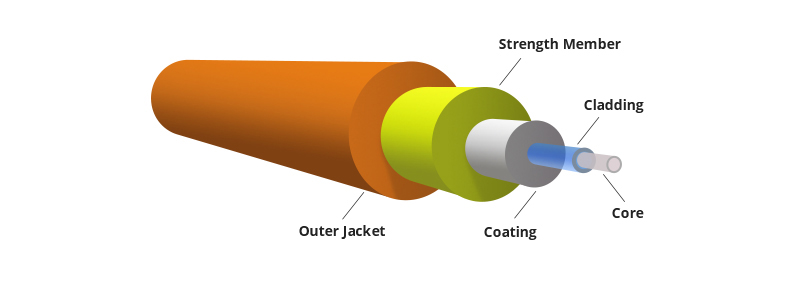
Figure 1: Optical fiber structure
Common Fiber Optic Cable Types
Generally, there are three types of fiber optic cables: the two glass optical fiber—single mode fiber optic cable and multimode optical fiber, as well as plastic optical fiber (POF).
Single Mode Fiber Optic Cable
The "mode" in fiber optic cable refers to the path in which light travels. Single mode fiber has a smaller core diameter of 9 microns (8.3 microns to be exact) and only allows a single wavelength and pathway for light to travel, which greatly decreases light reflections and lowers attenuation. Slightly more expensive than its multimode counterparts, single mode fiber optic cable is often used in network connections over long lengths.

Figure 2: Single mode fiber
Multimode Fiber Optic Cable
Multimode optical fiber has a larger core diameter than that of single mode fiber optic cable, which allows multiple pathways and several wavelengths of light to be transmitted. Multimode optical fiber is available in two sizes, 50 microns and 62.5 microns. It is commonly used for short distances, including patch cable applications such as fiber to the desktop or patch panel to equipment, data and audio/video applications in LANs. According to the fiber refractive index distribution, multimode fiber can be divided into two types: Step-Index Multimode Fiber vs Graded-Index Multimode Fiber.

Figure 3: Multimode fiber
Plastic Optical Fiber (POF)
POF is a large core step-index optical fiber with a typical diameter of 1 mm. The large size enables it to easily couple lots of light from sources and connectors that do not need to be high precision. So typical connector costs are 10-20% as much as for glass fibers and termination is simple. Being plastic, it is more durable and can be installed in minutes with minimal tools and training. For applications do not require high bandwidth over great distances, POF is more competitive, making it a viable option for desktop LAN connections and low speed short links.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Optical Fiber
Though optical fiber has speed and bandwidth advantages over copper cable, it also contains some drawbacks. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of optical fiber cable.
Advantages of Optical Fiber
Greater bandwidth & faster speed—Optical fiber cable supports extremely high bandwidth and speed. The large amount of information that can be transmitted per unit of optical fiber cable is its most significant advantage.
Cheap—Long, continuous miles of optical fiber cable can be made cheaper than equivalent lengths of copper wire. With numerous vendors swarm to compete for the market share, optical cable price would sure to drop.
Thinner and light-weighted—Optical fiber is thinner, and can be drawn to smaller diameters than copper wire. They are of smaller size and light weight than a comparable copper wire cable, offering a better fit for places where space is a concern.
Higher carrying capacity—Because optical fibers are much thinner than copper wires, more fibers can be bundled into a given-diameter cable. This allows more phone lines to go over the same cable or more channels to come through the cable into your cable TV box.
Less signal degradation—The loss of signal in optical fiber is less than that in copper wire.
Light signals—Unlike electrical signals transmitted in copper wires, light signals from one fiber do not interfere with those of other fibers in the same fiber cable. This means clearer phone conversations or TV reception.
Long lifespan—Optical fibers usually have a longer life cycle for over 100 years.
Disadvantages of Optical Fiber
Low power—Light emitting sources are limited to low power. Although high power emitters are available to improve power supply, it would add extra cost.
Fragility—Optical fiber is rather fragile and more vulnerable to damage compared to copper wires. You’d better not to twist or bend fiber optic cables too tightly.
Distance—The distance between the transmitter and receiver should keep short or repeaters are needed to boost the signal.
How to Select the Right Optical Fiber Cable?
Optical fiber cable has gained much momentum in communication networks, and there emerges a dazzling array of vendors competing to manufacture and supply fiber optic cables. When selecting optical fiber, you’d better start with a reliable vendor and then consider the selection criteria. Here’s a guide to clarify some of the confusions about choosing fiber optic cable.
Check Manufacturer Qualification
The major optical cable manufacturers should be granted ISO9001 quality system certification, ISO4001 international environment system certification, the ROHS, the relevant national and international institutions certification such as the Ministry of Information Industry, UL certification and etc.
Fiber Mode: Single Mode or Multimode
As illustrated above, single mode fiber is often used for long distances while multimode optical fiber is commonly used for short range. Moreover, the system cost and installation cost change with different fiber modes. You can refer to Single Mode vs Multimode Fiber: What’s the Difference? and then decide which fiber mode you need.
Optical Cable Jackets: OFNR, OFNP, or LSZH
The standard jacket type of optical cable is OFNR, which stands for “Optical Fiber Non-conductive Riser”. Besides, optical fibers are also available with OFNP, or plenum jackets, which are suitable for use in plenum environments such as drop-ceilings or raised floors. Another jacket option is LSZH. Short for “Low Smoke Zero Halogen”, it is made from special compounds which give off very little smoke and no toxic when put on fire. So always refer to the local fire code authority to clarify the installation requirement before choosing the jacket type.
Optical Fiber Internal Construction: Tight Pack or Breakout or Assembly or Loose Tube
Tight pack cables are also known as distribution style cables, features that all buffered fibers under a single jacket with strength members for Enclosure to Enclosure and Conduit under Grade installations. Breakout fiber cable or fan out cable is applicable for Device to Device applications with tough and durable advantages. Assembly or zip cord construction is often used for making optic patch cables and short breakout runs. While loose tube construction is a Telco standard used in the telecommunications industry.
Indoor vs. Outdoor
The choice greatly depends on your application. The major difference between indoor and outdoor fiber cable is water blocking feature. Outdoor cables are designed to protect the fibers from years of exposure to moisture. However, nowadays there have been cables with both dry water-blocked outdoor feature and indoor designs. For example, in a campus environment, you can get cables with two jackets: an outer PE jacket that withstands moisture and an inner PVC jacket that is UL-rated for fire retardancy.
Fiber Count
Both indoor and outdoor fiber cable have a vast option of fiber count ranging from 4-144 fibers. If your fiber demand exceeds this range, you can custom the fiber count for indoor or outdoor optical cable. Unless you are making fiber patch cords or hooking up a simple link with two fibers, it is highly recommended to get some spare fibers.
Conclusion
Optical fiber provides a fast, constant and stable Internet connection that allows a lot of data to be transmitted over incredible distances. As data demands become enormous, fiber optic cabling is the sure way to go for network flexibility and stability.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023















