Basic Knowledge About GPON SFP Transceivers
GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network. GPON is one of the key technologies that are being used in fiber-based (FTTx) access networks, including fiber to the home (FTTH), fiber to the business (FTTB), fiber to the curb (FTTC), etc. GPON system contains two main active transmission components, namely optical line termination (OLT) and optical network termination (ONT) or optical network unit (ONU). Modern OLT and ONT/ONU use compact fiber optic modules to achieve the triple-play GPON services. These modules are known as GPON SFP transceivers. This post will give a comprehensive introduction to GPON SFP modules.
What Is GPON SFP?
GPON SFP is one type of gigabit optical transceivers that are used in GPON system, which is compliant with ITU-T G.984.2 standard. It is a bidirectional module that has SC receptacle and works over simplex single-mode fiber optic cable. A GPON SFP module transmits and receives signals of different wavelengths between the OLT at the Central Office side and the ONT at the end users side. GPON SFPs utilize both the upstream data and downstream data by means of Optical Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM).
GPON SFP: Class B+ vs. Class C+
GPON SFP transceivers are categorized into GPON OLT SFP and GPON ONT SFP or GPON ONU SFP depending on the devices they are used in. And there are Class B+ GPON SFP and Class C+ GPON SFP. The major differences between them are the transmit power and the receive sensitivity. The table below lists the Tx power and Rx sensitivity of Class B+ GPON SFP and Class C+ GPON SFP.
| Transceiver Type | Class B+ | Class C+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tx power | Max. Rx sensitivity | Tx power | Max. Rx sensitivity | |
| GPON OLT SFP | 1.5-5 dBm | -28 dBm | 3-7 dBm | -32 dBm |
| OLT SFP Operation Wavelength | 1480-1500nm | 1260-1360nm | 1480-1500nm | 1290-1330nm |
| GPON ONT SFP | 0.5-5 dBm | -27 dBm | 0.5-5 dBm | -30 dBm |
| ONT SFP Operation Wavelength | 1260-1360 nm | 1480-1500nm | 1290-1330nm | 1480-1500nm |
By using Class B+ or Class C+ GPON OLT SFP, it can support up to 32 or 64 ONTs at customer premises respectively. And a C+ OLT SFP can be used with B+ ONT SFP as long as the loss budget of the link is appropriate.

Figure 1: GPON SFP Class B+ and Class C+
How’s the GPON SFP Different From Conventional BiDi SFP?
Although GPON SFP belongs to the gigabit BiDi SFP family, it differs from “normal” BiDi SFPs in some aspects. Here’s a comparison between GPON SFP transceiver and conventional BiDi SFP transceiver.
Signal Transmission Mode
In terms of conventional gigabit BiDi SFP transceivers that are mainly used in backbone network, the optical transmission mode is point to point (P2P), i.e., they must be used in matched pair. A BiDi usually has LC receptacle instead of SC receptacle. Here’s an illustration of P2P transmission mode.

Figure 2: Transmission mode of conventional SFP
The transmission mode of GPON SFP is point to multi-point (P2MP). One GPON OLT SFP at the Central Office communicates with multiple GPON ONU SFPs with the help of fiber optic splitters. This is why we usually see a GPON infrastructure is in a tree shape or a tee shape.

Figure 3: Transmission mode of GPON SFP
Transmission Distance
The transmission distance of conventional gigabit BiDi SFP can be up to 160 km over single-mode fiber cable when using 1590nm/1510nm and 1510nm/1590nm wavelengths. GPON OLT and ONT/ ONU SFP transceivers support a transmission distance up to 20 km with 1490nm/1310nm and 1310nm/1490nm wavelengths.
Benefits of Using GPON SFP
Using GPON SFP is considered a more convenient and cost-effective solution for the end customers. And it also reduces the devices that need to be provided by the Internet service provider (ISP). Before the GPON ONT SFP was released and used in GPON networks, the ISP usually needs to install at least an optical modem (a type of ONT with a fiber optic port) and an IP access router, and a Set-Top-Box or video recorder might also be needed if IPTV services are required. The separation of different devices inevitably increased the cost for GPON services.
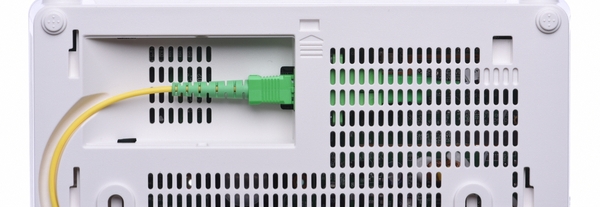
Figure 4: Optical modem with a fiber optic port.
The newly used GPON SFP is in smaller size and integrates the triple-play services. It has lower consumption as well. The ISP provides a GPON ONT SFP to the customer. This module is usually installed in the hub/router handed to the customer by the ISP. The customer is also able to unplug the fiber optic patch cable and the GPON ONT SFP from the ISP’s hub/router, and then plug them in his own router/switch that is white-listed by the ISP.
Conclusion
GPON SFP transceivers are typically used in the two main active transmission components OLT and ONT/ONU in GPON optical networks. They are essential in keeping the high-bandwidth communication between the service provider and the end users over a distance up to 20 km. GPON SFPs are classified into Class B+ and Class C+ and the main differences are their Tx power and Rx sensitivity. This module has simplified the implementation of GPON services. It benefits both the service providers and the end users to some degree.
Related Article: Understanding Video SFP Transceiver
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024














