DHCP vs Static IP: Which One Is Better?
Nowadays, most networking devices such as routers or network switches use IP protocol as the standard to communicate over the network. In the IP protocol, each device on a network has a unique identifier that is called IP address. The easiest method of achieving this was configuring a fixed IP address or static IP address. Since there are limitations to static IP, some administrators seek to use dynamic IP instead. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a protocol for assigning dynamic IP addresses to devices that are connected to the network. So DHCP vs static IP, what's the difference?
What Is a Static IP Address?
A static IP address is an address that is permanently assigned to your network devices by your ISP, and does not change even if your device reboots. Simply put, a static IP address is an IP address that does not change, like having a permanently fixed home address. This offers several advantages, such as simplifying network management, providing better reliability for services that require a stable IP, and avoiding problems that often occur with IP changes. However, precisely because the IP addresses are constant, they are more susceptible to hacking.
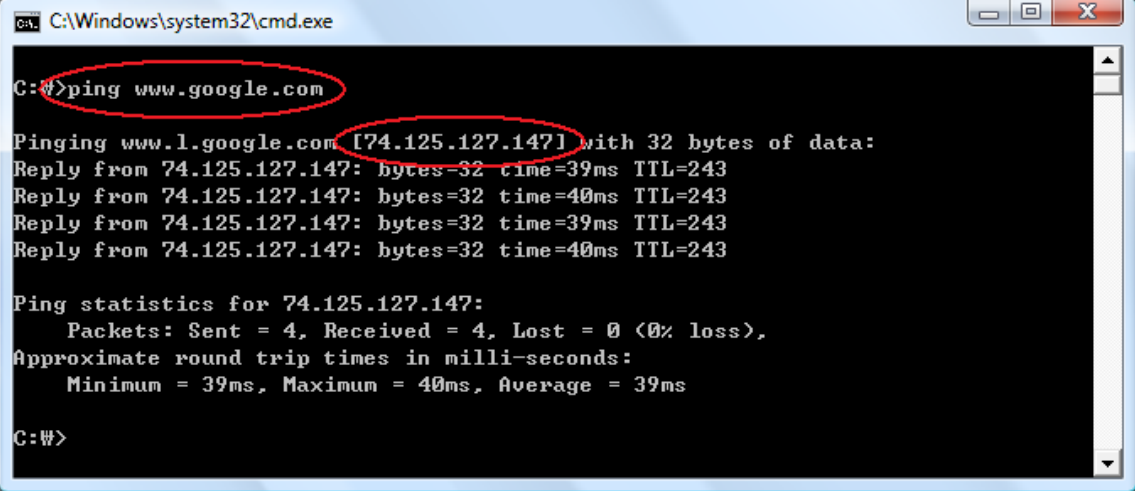
A typical example of using static IP address is web server. From the Window on your computer, go to START -> RUN -> type "cmd" -> OK. Then type "ping www.google.com" on the Command Window, the interface will pop up as you can see below. The four-byte number 74.125.127.147 is the current IP for www.google.com. If it is a static IP, you would be able to connect Google at any time by using this static IP address in the web browser if you want to visit Google.
What Is DHCP?
What is in contrast with the static IP address is the dynamic IP address. They are temporary and change every time you connect, similar to having a new home address each time. To create a dynamic IP address, the network must have a DHCP server configured and running.
As previously descrbed in the article "DHCP and DNS: What Are They, What’s Their Difference?", DHCP is a network management protocol used to automatically assign IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to network devices.
When a device connects to the network, the DHCP server automatically assigns it an available IP address from a predefined range, ensuring efficient IP address utilization and minimizing administrative overhead.

DHCP vs Static IP: Which One Is Better?
Proper IP addressing is essential for establishing communications among devices on a network. Then DHCP vs static IP, which one is better? This part will discuss it.
A static IP address assigns a fixed IP address to a network device, ensuring that it always has the same IP address. This is particularly beneficial for devices that require consistent and reliable connectivity, such as servers, printers, or mission-critical applications. However, network administrators must meticulously track each device with a static IP to prevent IP address conflicts. And since static IP address requires manual configurations, it can create network issues if you use it without a good understanding of TCP/IP.
DHCP is a protocol for automating the task of assigning IP addresses, which not only reduces the time it takes to configure and deploy devices, but also reduces the likelihood of configuration errors. This makes it ideal for environments where devices frequently join or leave the network, such as corporate offices or public Wi-Fi setups. Furthermore, DHCP is more cost-effective and requires less maintenance than static IP addresses.
| DHCP | Static IP | |
| Configure | DHCP does not need any manual configuration to connect to local devices or gain access to the Web. | Manually setting up each device is straightforward for a small number of devices, but it adds complexity when connecting a large number of devices. |
| Flexibility | Users can add or remove devices without altering the IP settings. However, the frequent changes in IP addresses can be unsuitable for applications that require a fixed IP, such as servers and printers. | Users must reconfigure IP settings whenever they add or remove a device, and as the network expands, they risk exhausting available IP addresses. |
| Management | DHCP streamlines the process of IP allocation and management. | Static IP requires manual IP assignment and tracking for each device, complicating network configuration and management. |
| Security | DHCP simplifies IP assignment and reduces human error but can be exploited by unauthorized servers, risking network invasions and unauthorized access. | Fixed IP addresses enhance access control and security but can cause IP conflicts and security breaches if mismanaged. |
| Cost | DHCP reduces the time and labor costs of manual configuration, but requires additional hardware or routers to run the server. | No additional hardware is required and configuration is done directly on the device. However, overhead costs are higher and more skilled personnel may be required, thus increasing labor costs. |
How to Choose Between DHCP and Static IP
Now that you have a clear comparison of DHCP vs. static IP, here are some guidelines to help you decide which is more suitable for your network needs:
Assess Network Requirements:
-
- If you have a large network with many devices frequently connecting and disconnecting, DHCP is your best bet.
-
- For small networks with critical devices needing constant access, static IP offer better reliability.
Consider the Role of Devices:
-
- Assign static IP addresses to servers, printers, and other critical devices that require consistent access.
-
- Use DHCP for user devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets, which benefit from dynamic IP assignments.
Future-Proof Your Network:
-
- If you expect your network to grow or undergo significant changes, DHCP provides the necessary flexibility.
-
- For stable environments that need consistent device addresses, static IP is the way to go.
By considering these factors, you can choose the method that best meets the needs of your network. Whether you are considering DHCP or static IP, having the right network equipment is critical. Whether opting for DHCP or static IP, having the right network equipment is crucial, and PicOS® switches excel in this regard. For example, the S5810-48TS-P supports DHCP, providing you with error-free network configurations, ensuring optimal network performance and ensuring seamless network management.
Conclusion
After comparing DHCP vs static IP, it is undoubtedly that DHCP is the more popular option for most users as they are easier and cheaper to deploy. Having a static IP and guessing which IP address is available is really bothersome and time-consuming, especially for those who are not familiar with the process. However, static IP is still in demand and useful if you host a website from home, have a file server in your network, use networked printers, or if you use a remote access program. Because a static IP address never changes so that other devices can always know exactly how to contact a device that utilizes a static IP.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024














