Forward Error Correction (FEC) in 100G Data Transmission
As bandwidth demands increase and the tolerance for errors and latency decreases, designers of data communication systems have been looking for new ways to expand available bandwidth and improve the quality of transmission. One solution isn't actually new but has been proven quite useful. It is called forward error correction (FEC), a technique that has been used for years to enable efficient, high-quality data communication over noisy channels. Today, with the increase in data transmission capacity and extension of distance, let’s learn more about FEC technique in optical networks.
What Is Forward Error Correction(FEC)?
Forward error correction (FEC) is a digital signal processing technique used to enhance data reliability. It does this by introducing redundant data, called error correcting code, prior to data transmission or storage. FEC provides the receiver with the ability to correct errors without a reverse channel to request the re-transmission of data. As we know, sometimes optical signals could deteriorate due to some factors during transmission, which may lead to misjudgment at the receiver end, possibly mistaking “1” signal for “0” signal, or “0” signal for a “1” signal. If the number of errors in transmission is within the correction capacity (discontinuous errors), the channel decoder will locate and correct the false “0” or “1” to improve the quality of the signal.
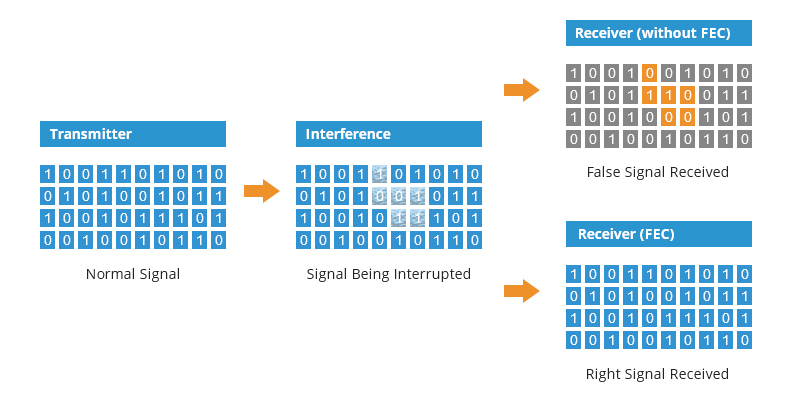
How Does FEC Work?
In optical communication systems, if an error arises in the link, the signal cannot be transmitted further. FEC technology involves encoding the signal to be transmitted into a code with a certain error correction capability at the FEC encoder at the transmitting end. The FEC decoder at the receiving end decodes the received sequence. If the number of errors generated during transmission is within its error correction capability (non-continuous errors), the errors are located and corrected. Consequently, FEC proves effective in reducing error rates, bolstering signal reliability within the system, and expanding the potential transmission distance.
Forward Error Correction(FEC) Types & Features
At present, the practical FEC technologies for SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) and DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) are mainly as follows: In-band FEC(coding gain is small 3-4dB)、Out-of-band FEC(5-6dB) and Enhanced FEC (EFEC).
-
FEC reduces the number of transmission errors, extends the operating range, and reduces the power requirements for communications systems.
-
FEC increases the throughput of the effective system, even with the extra check bits added to the data bits, by eliminating the need to re-transmit data corrupted by random noise.
-
FEC independently increases the reliability of data at the receiver.
Application of FEC in 100G Networks
In the context of fiber-optic networking, FEC is used to address optical SNR (OSNR) - one of the key parameters that determine how far a wavelength can travel before it needs regeneration. FEC is especially important at high-speed data rates, wherein advanced modulation schemes are required to minimize dispersion and signal correspondence with the frequency grid. Without the incorporation of FEC, 100G transport would be limited to extremely short distances. To implement long-haul transmission (> 2500 km), the system gain must be further improved by approximately 2 dB. FEC's upgrade from hard-decision to soft-decision fills this performance gap.
As the push for ever-higher transmission rates has continued, soft-decision forward error correction (SD-FEC) schemes have grown in popularity. Although these can require a byte overhead of around 20% — nearly three times as large as the original RS coding scheme — the gains they produce in the context of high-speed networking are substantial. FEC that results in a 1 to 2 dB gain on a 100G network, for instance, translates to a 20% to 40% greater reach.
Matters Needing Attention for FEC in 100G Networks
What to consider when configuring FEC in 100G networks? It is suggested to pay attention to the following tips.
Implementation Method
Some special modules have their own FEC functions, such as the FS 100G QSFP Single Lambda module. While other 100G QSFP28 optical modules mainly rely on FEC function configuration on the device to realize error correction, such as 100G switches.
Whether the Switch Supports FEC
The configuration of FEC on 100G switches can be achieved only if the switch supports it, and not all switches do so.
Whether to Enable FEC on 100G QSFP28 Transceivers
The FEC function is not just an advantage, the process of correcting error code will inevitably cause some data packet delay. Therefore, not all 100G QSFP28 transceivers need it. According to IEEE standard protocol, it is not recommended to enable FEC when using QSFP28-LR4-100G transceivers, except when it is recommended to enable it. Since the technology of 100G QSFP28 optical modules varies from company to company, the situation is not exactly the same. The following table explains whether it is recommended to enable FEC when using the FS 100G QSFP28 optical modules.
| Transceiver Type | Description | With FEC |
|---|---|---|
| QSFP28-SR4-100G | 850nm 100m MTP/MPO Transceiver Module for MMF | No |
| QSFP28-LR4-100G | 1310nm 10km Transceiver Module for SMF | No |
| QSFP28-PIR4-100G | 1310nm 500m Transceiver Module for SMF | No |
| QSFP-DR-100G | Single Lambda 1310nm 500m Transceiver Module for SMF | Yes |
| QSFP-LR-100G | Single Lambda 1310nm 10km Transceiver Module for SMF | Yes |
| QSFP28-IR4-100G | 1310nm 2km Transceiver Module for SMF | Yes |
| QSFP-4W10-100G | 1310nm 10km Transceiver Module for SMF | Yes |
| QSFP-ER4L-100G | 1310nm 40km Transceiver Module for SMF | Yes |
FEC Function Consistency at Both Ends of the Link
The FEC function of the port is part of the auto-negotiation. When auto-negotiation of the port is enabled, the FEC function is determined by negotiation at both ends of the link. If the FEC function is enabled at one end, the other end should also enable it, otherwise, the port is not up.
Stacking & Forward Error Correction(FEC)
Configuring the FEC command is not supported if the port is already configured as a physically stacking port. Conversely, ports that have been configured with FEC commands do not support configuring as a physical stacking member.
Conclusion
The role of FEC has become of critical importance in fiber optic communications, as backbone networks increase in speed to 40 and 100G, particularly as poor optical-signal-to-noise environments are encountered. Such environments become more commonplace in higher-speed environments, as more optical amplifiers are deployed in networks. With all these developments, FEC will continue to play a role in future networks. To ensure normal operation of the network, it is recommended that you pay special attention to the FEC function on optical modules, which will help you improve the performance in data transmission.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024














