How to Set up a 100G Metropolitan Area Network?
A metropolitan area network (MAN) has been adopted by various organizations of small or large sizes, including universities, city governments, and businesses with multiple buildings in a single geographical location. With the advent of 100G technology, the metropolitan area network has shifted from traditional 10G/40G to 100G Installations, therefore catering to the demands of increasingly growing data traffic volume.
Characteristics of 100G Metropolitan Area Network
Built upon the Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) metropolitan area network architecture, numerous metro networks thrive. In traditional 10G and 40G metro networks, operators typically choose between passive and fixed-filter technology or ROADM technology for deploying the optical network. The fixed-filter metro network offers low-cost, simple point-to-point connectivity but lacks flexibility and scalability. In contrast, a ROADM-based metro network provides easy-to-operate and flexible any-to-any connectivity, albeit with a higher initial installation cost.
Unlike 10G and 40G metro networks, the 100G metropolitan area network mainly uses the newly-developed coherent packet-optical technology which provides flexibility and scalability as much as the ROADM-based network but without its costly wavelength selective switches (WSS) and optical filters. With coherent technology, wavelengths in the 100G metro network can go from any site to any site, with any spectral width and centered on any frequency, making the network both flexible and future-proof. In addition, direct detect technology has also emerged as another solution for metro access Data Center Interconnectivity (DCI), particularly in DCI connections with spans less than 80km. For more details on coherent and direct technologies, please visit Direct vs. Coherent Detection.
Here are the main benefits of the 100G metro network with coherent packet-optical technology:
-
Higher capacity: The 100G metro network provides 100Gbps per fiber, allowing network operators to meet customers’ need for more bandwidth;
-
Cost-efficiency: Coherent technology in 100G metro network can help to continually reduce cost per bit via advanced technology innovations;
-
High competitiveness: The 100G metro network helps to increase the network provider’s competitiveness by doing more with less and the ability to turn up services faster.
-
Higher Network Security: The 100G metropolitan area network can more effectively support network security architecture, including encryption and identity authentication measures, to protect sensitive data and communications.
Setting up 100G Metropolitan Area Network
How to set up a 100G MAN network? There are two types of MAN networks: Wired metro network and wireless metro network. They use different forms of components and technologies. Here we will concentrate on 100G wired metropolitan area networks.
The first thing to set up a 100G metropolitan area network is to design a MAN network architecture. A metro transport network can typically be divided into three layers: national or core layer, regional layer and aggregation layer. And the last two layers provide transport functions within different technologies – IP RAN and PTN for mobile networks, and IP packet routing/switching for fixed broadband access. The key to designing a metropolitan area network is that on the premise of reducing overall cost as low as possible, the network system can meet the data capacity, the number of users, and the traffic needs as well as the ability to expand.
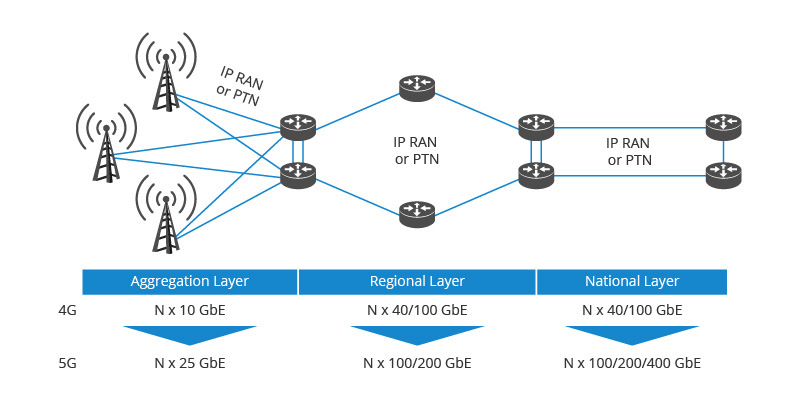
Figure 1: 100G Metro Transport Network Sublayers
100G Metropolitan Area Network Core Equipment
The foundation of a high-speed metropolitan area network (MAN) relies on its core equipment, which includes 100G DWDM CFP transceivers, optical amplifiers, and dispersion compensation modules. These components work together to ensure efficient and reliable internet connectivity within the network. The utilization of 100G DWDM CFP coherent optical modules enables seamless data transmission at 100G speeds, while optical amplifiers boost signal strength and dispersion compensation modules enhance signal clarity, collectively facilitating smooth high-speed data transmission in the MAN.
If you want to know more about the core equipment difference in the 100G metropolitan area network, you can check out this article: Key Technologies for 100G Metro Network Upgrades.
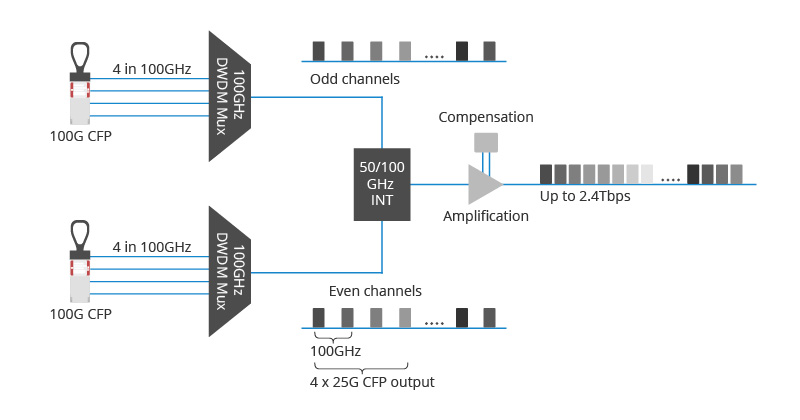
Figure 2: Basics of One Node in 100G Metro Network Core and Regional Layers
The End
Driven by the accelerating interest in 5G and cloud services, enhanced security through data replication, and growing media consumption, network hardware evolves to keep pace with the demand. Many service providers and data centers are jumping from 100G to 400G solutions. How will metropolitan area networks evolve in the following years when 100G is still being widely implemented today? Time will tell.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024
















