MACsec—a cool security option for your enterprise switch
Introduction
In somewhere intolerance of security risks, such as banks, military base, and government, there are a large number of confidential files. Besides the guard onsite, measures should be taken to maintain the network security as LAN is vulnerable to various security risks, and the economic loss caused by data leakage can be enormous. Thus, functions such as access terminals, port isolation, MACsec, IPsec, and TLS are developed to prevent hackers from intercepting sensitive data. And MACsec (Media Access Control security) can be deployed in the switches of these institutions to provide users with secure MAC layer data transmission and reception services. Next, we will put a brief look into what MACsec is, what advantages it has, and make some prospects for it.
What is MACsec?
Media Access Control Security (MACsec) is a network security standard that is defined as IEEE Standard 802.1AE. The MACsec protocol provides point-to-point security of data between Ethernet-connected devices and it can secure data communications between two devices without interfering with the number of devices or networks. When MACsec is enabled, the two connected devices exchange and verify security keys to establish a bidirectional secure link, and use a combination of data integrity checks and encryption to protect transmitted data. So, why should we choose MACsec, and how does it apply to a LAN? We will discuss it next. Below is a diagram of a typical LAN MACsec network.

The Advantages of MACsec
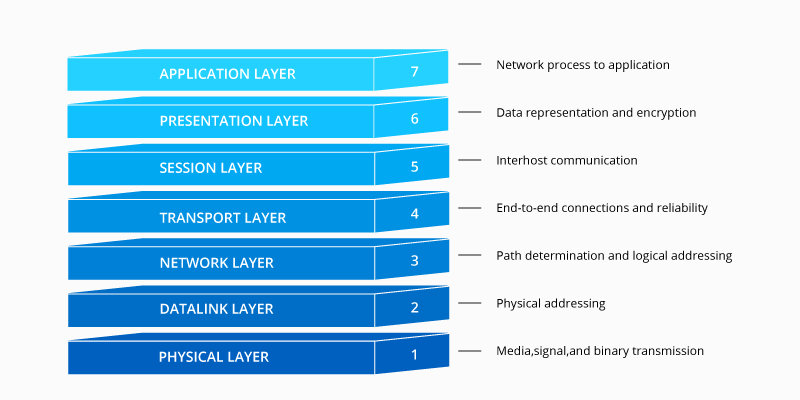
MACsec, relying on GCM-AES to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of all the network traffic, works at the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. Unlike protocols such as IPsec, which operate on Layer 3 as end-to-end technologies, MACsec decrypts each packet as it enters an Ethernet LAN and validates them when leaves an Ethernet LAN, so it can be said that the security of Layer 2 serves as a solid foundation for the entire networking system. Upper layer security mechanisms depend on the integrity of link layer activities and may not be able to detect whether communications have been compromised if without MACsec. The Layer 2 connection function is chosen to move packets around the data center to improve speed, minimize latency and reduce overhead data in packets. By contrast, if a secure Layer 3 technology such as IPsec is used, messages must be passed to the upper layer of the protocol for processing, which may increases latency. In addition, the Layer 2 solution avoids the complex task of creating a Layer 3 security policy.
To put it all into a nutshell, MACsec provides the following advantages:
-
MACsec supports line-rate encryption performance (40/100Gbps+)
-
MACsec can be deployed together with 802.1X and is more suitable for campus networks
-
MACsec can provide secure data transmission on a hop-by-hop device
-
MACsec is scalable and can be deployed in different ways
-
MACsec has low latency
How does MACsec Work?
MACsec functionality can be implemented between two devices or between client and devices. So, first, how does MACsec protect security when implementing between a device and client? MACsec refers to a series of trusted entities (SecY) made up of nodes on a network, where each node or SecY entity has a unique key linked to its Ethernet source address. MACsec is commonly used in conjunction with IEEE 802.1X-2010 or Internet Key Exchange (IKE) to achieve secure key distribution around the network, and it is suitable for Ethernet topologies such as star or bus LAN, and also supports point-to-point systems. In a MACsec-protected network, each node can receive both encrypted and plaintext messages, and system policies are used to specify how each message is processed. The kernel includes a bypass option for plaintext messages without authentication. As shown in the figure below, there are two switches connected. Important information is transmitted between the two devices, which requires the data communication between the two devices to be protected. Negotiation is processed between two switches' ports, after this, packet exchange is encrypted and decrypted. For example, MACsec encrypts plaintext 123 into *%&, transmitted to the port on the other switch and decrypted *%& into 123.

When implementing MACsec between two devices, the working process of MACsec protocol can be divided into three major phases, that is, session negotiation, secure communication, and session termination.
1. Session negotiation
Sessions are negotiated between devices via EAPOL-MKA (Extensible Authentication Protocol Over LAN-MACsec Key Agreement) messages using the configured Pre-Shared Key (PSK) as the CAK (secure Connectivity Association Key). The port with the higher priority between devices will be elected as the Key Server which is responsible for generating and distributing SAKs (Security Association Key), and the devices inform each other of their capabilities and the various parameters required to establish a session (such as priority, whether an encrypted session is expected, etc.) via the MKA protocol.
2. Secure communication
After the session negotiation is completed, each device has an available SAK and uses the SAK to encrypt data and start encrypted communication.
3. Session termination
When the device receives a downlink request from the other end, the security session corresponding to that user will be cleared immediately. After the MKA session timeout timer (default is 6 seconds, configurable) times out, if the MKA protocol message from the other end is still not received at this end, and the security session corresponding to that user will be cleared.
How to Give Full Play to MACsec, With the Use of IPsec
MACsec is for authentication and encryption of traffic over Ethernet on Layer 2 LAN networks. IPSec, on the other hand, is utilized for Layer 3 networks. IPsec works on IP packets at Layer 3, while MACsec operates on Ethernet frames at Layer 2. MACsec can secure all DHCP and ARP communications that IPsec can't. MACsec is limited to switches or end-nodes on a LAN to some extent, whereas IPsec can work across a wide area network (WAN) for routers.
Either one of them cannot help the security system resist all attacks. In practice, we should choose the appropriate protocols according to different situations and pay attention to strengthening the interoperability and complementarity between protocols to further improve the security of the network. MACsec should never be thought of as a replacement for IPSec, but rather another set of tools in the encryption tool bag moving forward, and in some cases, deployed in combination with IPsec in larger-scale deployments.
Conclusion
As mobile devices, video traffic, and cloud service continue to expand, the bandwidth demands are increasing fast accordingly so that the network environment has also become complex. The issue of data security and privacy has become particularly significant. Institutions with high requirements for data security and privacy all need to pay attention to LAN security. And the switch, as the most basic equipment for building a LAN, deploying more appropriate security protocols to your enterprise switch can more effectively avoid data risks and protect your LAN security. MACsec is the new choice for enterprises, governments, or service providers working on the next generation of high-speed encryption. If you have such a need, MACsec can be a cool option. If you want to know more about how to deploy enterprise switches to protect your data, please contact us here or visit FS.com.
Related Article:
TCP/IP vs. OSI: What’s the Difference Between the Two Models?
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024













