Taking an In-depth Look at DWDM Transceivers
It is no exaggeration to say that the advent of DWDM technology has almost changed the landscape of optical networks. With DWDM transceiver being one of its most important components, DWDM network has been widely employed in many different industries and areas to boost network capacity.
What Is DWDM Transceiver and How Does It Work?
DWDM transceiver functions just as other standard optical transceivers - to convert electrical signal to optical signal and then to electrical signal. The difference is that DWDM transceiver leverages DWDM technology to multiplex different wavelengths or several optical signal onto a single fiber to save valuable fiber resources. It is designed for single-mode fiber and operates at a nominal DWDM wavelength from 1528.38 to 1563.86 nm (Channel 17 to Channel 61) as specified by the ITU-T. Except from being applied in long distance transmission, DWDM transceivers can also be used in switch to switch interface, switched backplane applications and router/server interface etc. DWDM transceiver supports up to 10 Gbps and can span a distance up to 120 km, which makes itself optimal for high-capacity and long-haul transmissions.
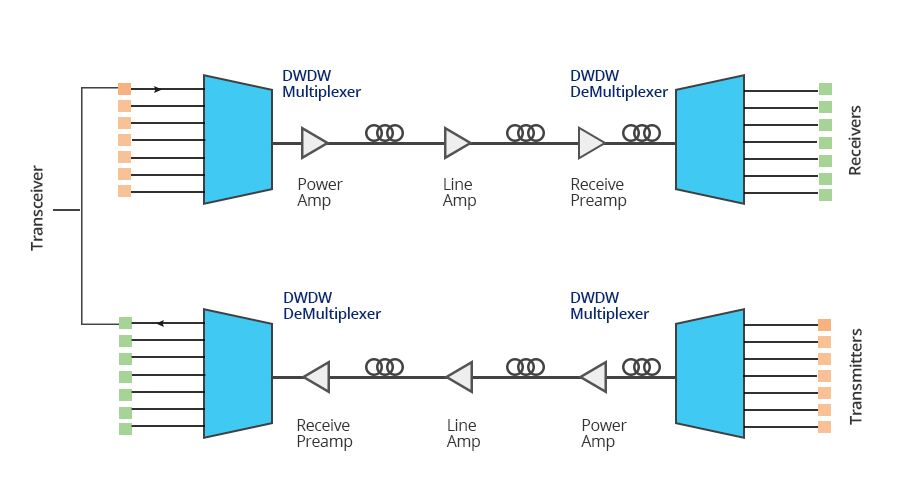
Figure 1: DWDM Transceiver Working Principle
Common DWDM Transceiver Types
DWDM transceivers are available in different types, supporting transmission rate from 155 Mbit/s to 10 Gbit/s. Categorized by data rates and form factors, there are DWDM SFP transceiver, DWDM SFP+ transceiver, DWDM XFP transceiver, etc. as following.
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| DWDM SFP | DWDM SFP transceivers provide a high-speed serial link at signaling rates from 100 Mbps to 2.5 Gbps. The DWDM SFP modules meet the requirements of the IEEE802.3 Gigabit Ethernet standard and ANSI Fibre Channel specifications, and are suitable for interconnections in Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel environments. |
| DWDM XENPAK | DWDM XENPAK is an important step in the evolution. It is the first 10GbE transceiver ever to support DWDM. DWDM XENPAK transceiver supports 32 different channels for up to 200 km with the aid of optical amplifiers known as EDFAs. |
| DWDM X2 | DWDM X2 transceiver is a high performance, serial optical transponder module for high-speed, 10G data transmission applications. The optical module is fully compliant to IEEE 802.3ae standard for Ethernet, making it ideally suited for 10GbE datacom applications. |
| DWDM XFP | DWDM XFP transceiver complies with the current XFP MSA specification. It supports SONET/SDH, 10GbE and 10-Gigabit Fibre Channel applications. It is small in size and cheap in price. |
| DWDM SFP+ | DWDM SFP+ is specifically designed for carriers and large enterprises that require a scalable, flexible, cost-effective network system. It is even smaller than the previous XFP and is the ideal choice for 10G highest-bandwidth application. |
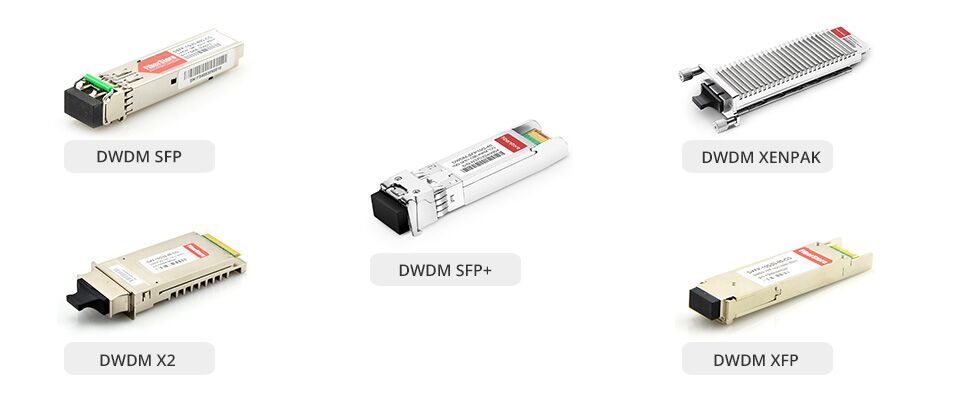

Figure 2: DWDM Transceiver Evolvement
As for fixed or tunable wavelength, DWDM transceiver can be divided into fixed wavelength DWDM transceiver and tunable DWDM transceiver. Fixed wavelength DWDM transceiver can only transmit a certain number of wavelength, usually at 1310nm and 1550nm for 10G data transmission applications. The tunable DWDM transceiver, however, enables flexible selection of working wavelength or channel. Typically these tunable DWDM optics are for the C-Band 50GHz. Around 88 different channels can be set with intervals of 0.4nm. Tunable transceivers are typically used as “spare-optics” in case of emergency.
So why tunable DWDM transceivers are needed? As the technology develops, hundreds of different wavelengths in DWDM 50GHz have been adopted, a large quantity of backup DWDM optical modules are needed for additional protection. And tunable DWDM transceiver modules are the choices. Besides, it is common to stock fixed wavelength DWDM transceivers at hand in case of emergency such as network downtime, but we can’t predict which specific channel is needed. Tunable DWDM transceivers enable flexible wavelength assignment based on your demand while saving fiber optics resources.
The Current Status and Applications of DWDM Tunable Transceivers
The rapid growth of network traffic has led to the evolution and upgrading of the data center, thus bringing great opportunities for the optical transceiver industry. As the core component in long-haul and high-capacity optical network, DWDM transceivers are also developing with new ideas, new technologies such as simplified packaging, smaller size, higher speed and lower power consumption. DWDM transceiver is widely applied in telecommunications and cable companies and is an integral part of their core networks. Or any organizations running densely populated data centers, particularly hyperscale cloud service providers for their infrastructures or colocation providers for their densely multi-tenanted spaces.
-
The 5G front-haul network promotes the demand for DWDM optical modules. The explosion of data traffic and accelerated deployment of 5G and Internet of Things will further fuels the deployment of high-speed WDM optical modules, and the demand for DWDM modules in long-haul transmission is huge.
-
The rise of the data market also drives the demand for high-speed DWDM transceiver modules. The platform using cloud technology such as AI, video, online games and other technologies will continue to drive the demand for DCI. And in the flow between very large data centers needs DWDM transceiver to maximize efficiency and handle the huge computing needs of enterprises.
Summary
No matter how fast the Internet technology grows and how advanced the technology will be in the future, optical transceivers will continue to be a indispensable part for optical transmission system. Where there is a need, there is a market. DWDM transceivers have been widely adopted during the past years, which will continue to get upgraded and developed in the following years. Although the market share for DWDM tunable transceiver is not big enough, we can still see huge potential from its application. To tune or not to tune, that’s a question depends on yourself.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023














