Telemetry and SNMP: Key Tools for Remote Monitoring and Management
Telemetry and SNMP serve critical roles in the world of network management, but they cater to different use cases and data types. Understanding their differences can help you make an informed decision when selecting the appropriate tool for your monitoring and management needs.
What Is Telemetry and SNMP in Networking?
Telemetry is the next-generation network monitoring technology used to remotely collect data from devices at high speed. Devices periodically push device information to collectors, providing real-time, high-speed, and accurate network monitoring. Specifically, Telemetry organizes data based on YANG models, encodes data in Google Protocol Buffers (GPB) format, and transmits data through the Google Remote Procedure Call (gRPC) protocol. This enhances data collection efficiency and promotes intelligent connectivity.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet standard used for monitoring and managing IP-connected network devices like routers, switches, firewalls, servers, and more. It collects and transmits data from these devices, facilitating network monitoring and fault detection, ensuring seamless communication between monitored devices and the monitoring systems.
The Advantages of Telemetry and SNMP
Telemetry
-
1. Fine-Grained Monitoring: High precision and rich data types are collected, providing a comprehensive reflection of the network's status.
-
2. Rapid Fault Localization: In complex networks, users want to quickly locate faults within seconds or even sub-seconds.
-
3. Proactive Data Reporting: In telemetry, a single subscription is all it takes for devices to continuously report data, alleviating the burden of processing query requests on devices.
SNMP
-
1. Network administrators can utilize the SNMP platform to perform tasks such as information querying, modification, and troubleshooting at any point on the network, improving efficiency.
-
2. Shielding physical differences among various devices to achieve automated management of products from different manufacturers.
How Does Telemetry and SNMP Work?
Telemetry is a closed-loop automated operations system, also known as an intelligent operations system. It consists of components such as network devices, collectors, analyzers, and controllers. The implementation of a telemetry system involves five stages:
-
1. Subscribe to Data Collection: Device data to be collected and pending data to be collected need to be subscribed.
-
2. Push Collected Data: Devices send the collected data to the collector based on the data subscription method. The collector then receives and stores the data.
-
3. Read Data: The analyzer reads the collected data stored in the collector.
-
4. Analyze Data: The analyzer analyzes the collected data and sends the analysis results to the controller for network configuration, management, and optimization..
-
5. Adjust Network Parameters: The controller deploys the adjusted network configuration to the devices. Once these configurations take effect, the devices report newly collected data to the collector. The analyzer assesses whether the network optimization results meet expectations. Once optimization is complete, the service process concludes.

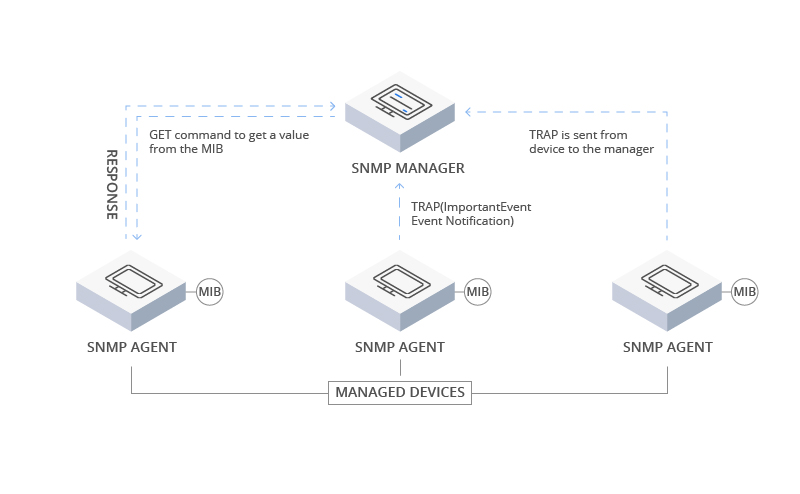
SNMP operates by sending Protocol Data Units (PDUs) to network devices that respond to SNMP. All of this communication is monitored, and network monitoring tools use GET requests to retrieve data via SNMP. Traffic enters the network from various sources, and the Simple Network Management Protocol communicates with the entire network and its devices.
SNMP is pre-configured on devices and, once enabled, stores performance statistics. Each network server has multiple Management Information Base (MIB) files. Monitoring data is obtained by querying the device's MIB files, and SNMP's operation revolves around its components, contributing to resource management.
Telemetry vs. SNMP
|
Telemetry
|
SNMP
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
HOW IT WORKS
|
Push model continuously sends device operational data to management system
|
Polling mechanism collects device performance data and returns data to management platform
|
|
PROTOCOLS USED
|
User Datagram Protocol or TCP
|
User Datagram Protocol
|
|
USE CASES
|
Collecting high-resolution performance data, such as high-speed network interface statistics
|
Retrieving static data, such as inventory or neighboring devices
|
|
BENEFITS
|
Sends data at higher rate; more efficient and practical
|
Simple protocol and easy to perform ad hoc data collection; widely supported by network devices and monitoring platforms
|
|
CHALLENGES
|
Telemetry that relies on TCP connections can use large amounts of memory
|
Management system repeatedly creates and sends data requests to each device
|
Conclusion
Telemetry and SNMP are integral tools for effective network monitoring and management. While Telemetry is more versatile and ideal for diverse applications, SNMP remains a reliable choice for network-specific tasks. The selection of the right tool depends on the specific requirements and objectives of your network management and monitoring needs.
FS provides cost-effective switches with SNMP support for efficient network management, suitable for various scenarios, such as S3400-48T6SP, S3400-24T4FP, S3260-16T4FP, S5500-48T6SP-R, etc. You can select and purchase FS switches based on your requirements.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023
















