Transformer-Free UPS vs Transformer-Based UPS Design Comparison
Since transformer-free UPS design came to the attention of the public in the early years of this century, it has earned its place in the UPS market with its small size and low cost. It seems to be a huge hit to the conventional transformer-based UPS market, however, transformer-based UPS is not utterly useless, on the contrary, extremely crucial and irreplaceable for some applications. This post will look at the difference between the transformer UPS and transformerless UPS.
Why UPS Design Evolves From Transformer to Transformerless?
The reason why an internal transformer is used in the early UPS system is the power inverter technology used in the UPS design. In the early days, the inverter was based on the silicon controlled rectifiers/thyristors to generate the sine wave output through significant filtering. (In a double conversion mode, UPS system with isolation transformers traditionally use 6- or 12-pulse thyristor rectifier topologies.) The power devices do not turn off when supplied from DC and since the switching speed of the power devices is slow, it requires a transformer to generate the desired waveform. With the development of technology, though transistors are developed to be switched on and off without the provision of additional power circuits, the operating volts are sacrificed to achieve the increase in switching current. Transformer is also needed to help step up the voltage of the UPS output to provide the critical load with the same voltage rating of the input.
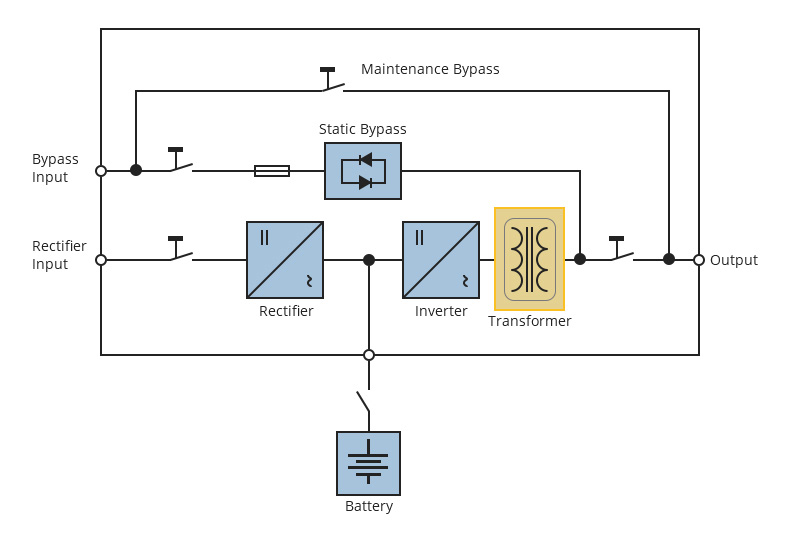
Figure 1: Diagram of transformer-based UPS
As the further development in power switching devices, insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) comes into use. UPS inverters based on IGBT technology utilize pulse-width modulation to generate the desired sinewave, eliminating the use of bulky transformer and filter. With the IGBT design, the transformer-free UPS is more effective in directly converting DC to AC, which contributes to a more stable output voltage.
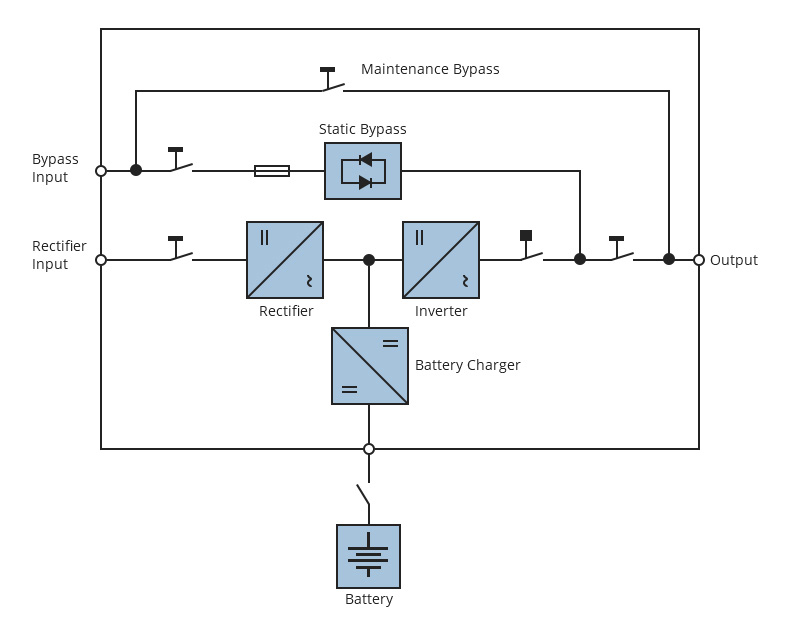
Figure 2: Diagram of transformer-free UPS
Technical Differences Between Transformer-Based UPS and Transformer-Free UPS
Apparently, the most significant distinction between transformer-free and transformer-based UPS is the existence of the transformer component. To know better about their technical features and performance, the following comparison on technical features is listed.
| Transformer-based UPS | Transformer-free UPS | |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency on double conversion mode | 90-92% | 95-96% |
| Efficiency on eco-mode | 99% | 99% |
| Total harmonic distortion of the input current (THDi) | 3-4% (IGBT-based rectifier)12% (12-pulse thyristor-based rectifier)30% (6-pulse thyristor-based rectifier) | 3-4% |
| Total harmonic distortion of the output voltage (THDU) | 2% | 2% |
| Input power factor (Input PF) | Low on partial load | 0.99-0.97 at full and partial load |
| AC ripple on battery | More than 5% without battery charger;0.2% with battery charger | 0.2% |
| Bypass function | Static bypass switch | Static bypass switch, but the bypass AC input must be the same as inverter AC output |
| Output impedance | High | Low |
| Dynamic response | Poor, unbalanced loads affect outputvoltages | Ideal, direct control of the output sine wave, each phase is controlled independently. Thus, unbalanced loads donot affect the output voltages |
| Weight and Size (500kVA unit) | 2.2-2.6 tonnes and 1.8-2.0㎡ | 1 tonne and 1.5-1.6㎡ |
Which Is Better: Transformer-Based UPS or Transformer-Free UPS?
Having referred to the technical differences between transformer-free UPS and transformer-based UPS, the following part will compare the two UPS designs from the perspective of the consumers and clarify their advantages.
Adaptability:Transformer-free UPS provides greater flexibility and adaptability in accommodating uncertain future requirements. The size of a transformer-free UPS is usually smaller than an equal power-rated transformer-based one. It is more convenient for expansion in a given space. In addition, Currently, large transformer-free UPS adopts modular design in a compact package so that the capacity can be easily added if the total load requirement is unsure or in case of future needs.
Reliability: Transformer-free UPS is not able to isolate the internal faults like a transformer-based one. Though this problem can be solved by adding an isolation transformer, it may also lead to other points of failure and higher unit service rates. Benefit from the isolation transformer within a transformer-based UPS design enhancing the reliability of the DC link and the years of application experience and technology innovations, transformer-based UPS shows higher reliability and robustness.
Availability: Generally transformer-based UPS provides the highest availability while simplifying fault current control, especially for high power data centers and other critical applications. Nowadays transformer-free designs also improve their availability to a reasonable level, however, less compared to the transformer-based models. Thus transformer-free UPS is more viable for those small or medium businesses where availability is not the top concern.
Battery life: The battery life is connected to the AC ripple on the battery. Because of the high voltage in transformer-free UPS, generally, there is an extra converter added in the transformer-free design, providing precise control of the batteries and a clean DC circuit with no ripple. Thus the battery life of transformer-free UPS is longer than the transformer-based one and can reach up to 12 years.
Cost: When it comes to the cost of UPS power units, the initial upfront cost and the operating cost are both needed to be considered. Due to the lack of transformer installed within it, the transformer-free UPS has an inherent benefit of a less expensive price than the transformer-based models. Transformer-free UPS also has a smaller size than transformer-based UPS, reducing the need for extra space in the data center. Operating costs include the operating expenses to power, the expenses for maintenance and others. Transformer-free UPS units show higher efficiency, thus reducing power losses.
Summary
Both transformer-based and transformer-free UPS designs provide fundamental functionalities and keep their main characteristics. It is clear that transformer-free UPS dominates the market these days, transformer-free UPS matches the majority of today‘s power supply design requirements, but for applications requiring the highest reliability and safety such as medical fields, transformer-based UPS is the best choice.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023














