Unveiling the Guardian of Cybersecurity: Network Firewall
In the digital age, with the pervasive exchange of information and data, network security has become paramount. Firewalls often cybersecurity heroes, act as the initial defense against an array of online threats and unauthorized access attempts. Derived from the concept of physical network firewalls, which prevent the spread of fires within buildings, their digital counterparts are essential for safeguarding interconnected systems, from individual computers to corporate networks and government infrastructures.
What is a Network Firewall?
A network firewall, whether for enterprise or personal use, is a network security device that enforces pre-established security policies by monitoring and filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic. Essentially, it acts as a protective barrier separating a private internal network from the public Internet. Its core role is to permit safe traffic while blocking potential threats. Firewalls come in various forms, including hardware, software, software-as-a-service (SaaS), and public or private cloud solutions. They are a critical element of network security, with third-party firewall applications often offering enhanced protection compared to basic built-in firewalls found in most operating systems.

Network Firewall Features and Capabilities
Because it delegates host-level safeguards to your network security device, a network firewall is an essential component of any security strategy. They can create policies to better protect your network and do quick assessments to detect and stop unwanted or unexpected activities, such as malware.
Threat Defense
Network firewalls can incorporate a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) strategy into modern organizational cybersecurity devices, whether deployed at the network perimeter to defend against external threats such as malware attacks and hacking shots, or within the network to establish segmentation and protect against insider threats.
Logging and Audit Functions
Firewalls log events, which administrators can utilize to spot patterns and improve rule sets. To stay up with ever-changing cybersecurity risks, rules should be modified regularly. Vendors identify new threats and create fixes to address them as quickly as possible.
Traffic Filtering
Network firewalls can filter traffic and notify the user of intruders in a single home network. They're especially handy for always-on connections, such as DSL or cable modems, because those sorts of connections employ static IP addresses. A Firewall ensures that only planned and nondestructive internet content is allowed to flow through.
Controlling and Blocking Access
To prevent unauthorized use, firewalls can be used to regulate and block access to specific websites and online services. For example, an organization can deploy a network firewall to prevent employees from accessing problematic websites when browsing the internet.
Secure Remote Access
Network firewalls play a crucial role in network security by offering secure remote access through virtual private networks (VPNs) and other remote access technologies. Whether in business or home environments, they are a key component of cybersecurity, often integrated into a comprehensive security information and event management (SIEM) strategy. You can easily acquire firewalls through popular technical service platforms like FS.com.
How Does a Network Firewall Work?
Network firewalls are placed inline within a network connection, scrutinizing all incoming and outgoing packets within the secured network. During inspection, they rely on predefined rules to differentiate between harmless and malicious traffic or packets.
The term "packet" denotes a data segment formatted for internet transmission. Packets encompass the data itself along with associated information, such as its origin. Firewalls leverage this packet data to determine compliance with the rule set. Non-compliant packets are denied entry into the protected network.
Rule sets can be constructed based on various packet data aspects, including source, destination, and content. These attributes may be interpreted differently at different network levels. As a packet traverses the network, it undergoes multiple reformattings to guide the protocol in directing it. Different types of firewalls are designed to inspect packets at various network layers.
Types of Network Firewalls
Firewalls can take several forms and perform a variety of tasks. Examples of this include the following common types:
Next-generation Firewall (NGFW)
Firewalls have evolved beyond basic packet filtering and stateful inspection. Many organizations now implement NGFWs to combat contemporary threats such as advanced malware and application-layer attacks. According to Gartner, Inc.'s criteria, a next-generation firewall must encompass:
-
Intelligence-based access control with stateful inspection
-
Integrated intrusion prevention system (IPS)
-
Application awareness and control for identifying and blocking risky applications
-
Pathways for future information feeds through upgrades
-
Strategies to tackle evolving security threats
-
Geolocation and reputation-based URL filtering
Besides, these NGFWs support the update and use of intrusion prevention systems (IPS), antivirus (AV), URL filtering, quality of service (QoS), and threat intelligence (TI) through license and subscription services. While these features are increasingly becoming the standard for most organizations, NGFWs offer additional capabilities. Discover more about Security Solutions with NSG Series NGFW.
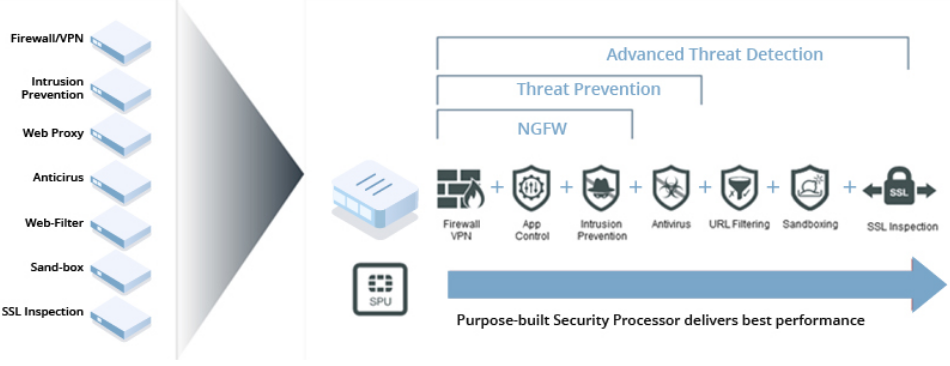
Unified Threat Management (UTM) Firewall
A UTM device often combines the tasks of a firewall with stateful inspection with intrusion prevention and antivirus in a loosely connected manner. It may also contain extra services and, in some cases, cloud management. UTMs promote simplicity and usability. Moreover, UTMs promote simplicity and usability, offering the following benefits:
-
All-in-One Protection
-
Simultaneous Security
-
Intrusion Prevention
-
Email Security
-
Centralized Control
Cloud Native Firewall
Cloud-native firewalls are transforming the way apps and scalable workload infrastructure are protected. These firewalls enable networking and security operations teams to operate with greater agility by leveraging their automatic scaling capabilities, giving the following important benefits:
-
Agile and flexible security
-
Support for multiple tenants
-
Intelligent load balancing
Conclusion
Network firewalls are a crucial defense for networks and systems, protecting them from all incoming traffic, whether harmless or harmful. While connecting personal computers to the internet has benefits, it also exposes them to common risks like hacking, identity theft, malware, and online fraud. Unprotected networks and devices can be easily discovered and accessed by malicious individuals, especially with continuous internet connections. To address these risks, proactive protection is essential, with firewalls playing a key role in network defense.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024













