WDM vs. OTN, What's Your Choice?
In the rapidly advancing field of telecommunications, the need for high-speed data transmission and effective network management has led to the creation of cutting-edge technologies. Among these, Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) and Optical Transport Network (OTN) stand out as transformative solutions. This article will explore the attributes, capabilities, and distinctions of WDM and OTN, highlighting their specific features that make them integral to modern telecommunication systems.
Overview of WDM and OTN Technology
What Is WDM?
It might be better to understand WDM with an example. In a WDM system, optical fiber is an highway and the light waves for transmitting services are trucks. As to different transmission signals such as news, blogs or vedios are like packages to be transported. These packages are directly placed on different trucks. If all these trucks want to enter the optical fiber transmission regardless of the lanes, then crowding in will cause chaotic traffic flow on the entire expressway and affect transmission efficiency. Is there any way to avoid this phenomenon? The answer is WDM. With WDM, different transmission data can be realized simultaneously on the same optical fiber, which is equivalent to dividing lanes for different vehicles on the highway, allowing different vehicles to run on separate lanes at the same time, improving transmission efficiency.
Figure1. Function Of WDM
Meanwhile, to ensure smooth traffic, it is necessary to distinguish lanes so that different vehicles can go their own way. Similar to the division of large and small lanes on streets, the WDM system can be divided into two types: CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) and DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) . The former has a relatively large lane interval (wavelength interval), generally 20 nm, while the latter has a small interval, generally less than 0.8 nm. You can read this article to know more about WDM technology: WDM Basics: Understanding Wavelength Division Multiplexing Technology
In a WDM system, services are first directed to dedicated vehicles (OTU units) where they are converted into standard wavelength optical signals recognizable by WDM. These optical signal vehicles then proceed to checkpoints (Mux units), where they are directed into different lanes and sequentially transmitted on the network. A monitoring channel (patrol car) ensures smooth transmission. For long-distance travel, vehicles enter optical amplifier units (unified gas stations) to regenerate and amplify signals to maintain signal integrity. Upon reaching the terminal station, vehicles exit checkpoints (Demux units) and are routed to corresponding client terminals. Here, services are unloaded, converted into client service signals (without wavelength information) by OTU, and delivered to clients.

Figure2. Work Process of WDM
What Is OTN?
With the development of communication networks, digital traffic has increased rapidly. So experts had to continue to develop the potential of WDM and improve its capabilities. A new technology was born - OTN.
OTN is a telecommunications industry standard protocol, defined in various ITU Recommendations, such as G.709 and G.798—that offers an efficient way to transport, switch, and multiplex different services onto high-capacity wavelengths across the optical network. The OTN technology provides a network-wide framework that adds SONET/SDH-like features to WDM equipment. To find out more information about OTN, you can read this article: What Is OTN—Optical Transport Network?
WDM vs. OTN, What're the Differences?
Networking Mode
The networking mode of WDM is basically point-to-point, chain, star and ring networking. The networking mode of OTN is usually a ring network, mesh network and other networking modes.
WDM multiplexes optical signals of different wavelengths into one fiber for transmission. There are two modes: DWDM and CWDM. Currently, DWDM is the mainstream. the mainstream WDM systems are 40-wavelength and 80-wavelength systems (which are being converted to more than 96-wavelength and 120-wavelength systems) that carry more wavelengths. OTN is asynchronous mapping of payloads.
Components
WDM mainly contain multiplexer, demultiplexer, amplifier and ROADM. While OTN, composed of optical cross-connector (OXC) and optical add/drop multiplexer (OADM), possesses functions like optical cross-ability and wavelength conversion.
Error Correction and Network Intelligence
WDM systems lack built-in error correction mechanisms, whereas OTN integrates robust forward error correction (FEC) algorithms, ensuring reliable data transmission despite noise and signal degradation. Additionally, OTN offers advanced management and monitoring capabilities, enabling network operators to efficiently detect and troubleshoot issues. These features, which provide enhanced reliability and operational efficiency, are absent in traditional WDM systems.
Network Scalability
WDM offers scalability by increasing the number of wavelengths to support higher data rates, but this often requires complex reconfigurations and adjustments. In contrast, OTN provides inherent scalability through flexible bandwidth provisioning and efficient traffic grooming. This enables dynamic allocation of network resources, allowing for easier adaptation to changing demands and future growth, thereby simplifying the scaling process compared to traditional WDM networks.
Application Scenarios
WDM is mainly used in inter provincial trunk network and intra provincial backbone network. OTN provides a very ideal solution for large broadband granular services.
OTN vs. DWDM
As for OTN vs. DWDM (one important technology of WDM) or DWDM vs. OTN, there are the differences between OTN and DWDM. Although the DWDM system greatly improves the transmission efficiency of optical fibers and supports large-granularity services, its point-to-point wavelength configuration limits dynamic adjustment, leading to low resource utilization and inflexible service adjustments. Network management in DWDM is limited to monitoring the optical layer, with minimal troubleshooting methods and high maintenance difficulty. In contrast, OTN inherits DWDM's large-capacity transmission and adds flexible optoelectronic joint scheduling and protection capabilities. By incorporating ROADM technology, OTH technology, G.709 encapsulation, and control planes, OTN overcomes traditional WDM network limitations, offering sub-wavelength service scheduling, strong networking, and protection capabilities. OTN supports high bandwidth utilization with detailed overhead bytes and enhanced OAM/P functions. Additionally, OTN and DWDM can share the optical layer, but OTN includes an electrical layer subframe, allowing existing DWDM devices to upgrade to OTN with electronic cross-connect sub-frames.
Is OTN Superior to WDM?
As mentioned above, WDM system is similar to highway traffic system, while OTN is an upgraded version of highway traffic system. Is OTN technology superior to WDM? What kinds of advantages are OTN over WDM?

Figure3. WDM and OTN System Comparison Diagram
OTN Support Monitoring, Management, Operation and Maintenance
From the above figure, it can be seen that signals are converted into services with wavelength information before being transmitted into the WDM system. In other words, the WDM system has no supervision mechanism for transmitted services. It only guarantees that the signals can be transmitted to the receiving end.
While in the OTN system, a set of rules is provided for signals, which is also known as the frame structure requirement. Signals entering the OTN system are first packaged according to the OTN frame structure requirements, that is adding information on monitoring, management, operation and maintenance, and then transmitting the converted signals with wavelength in the OTN system.
OTN Support Electrical Crossover Function
By adding the electrical crossover function, OTN system can process client service signals and WDM signals separately.

Figure4. Electrical Crossover of OTN
In the WDM system, client services are transmitted after converting their signals into WDM signals. Traditionally, this conversion is directly handled by the same single board, requiring a dedicated light wave for each client service. As network complexity grows with more service types, this approach necessitates developing new boards to accommodate them, raising construction costs and intensifying resource allocation challenges due to increased light wave usage. Hence, OTN introduces an electrical crossover function akin to a centralized cargo dispatch center in traditional WDM. This dispatch center efficiently bundles and directs various services entering the OTN system onto separate "vehicles" carried by distinct light waves, optimizing resource utilization.
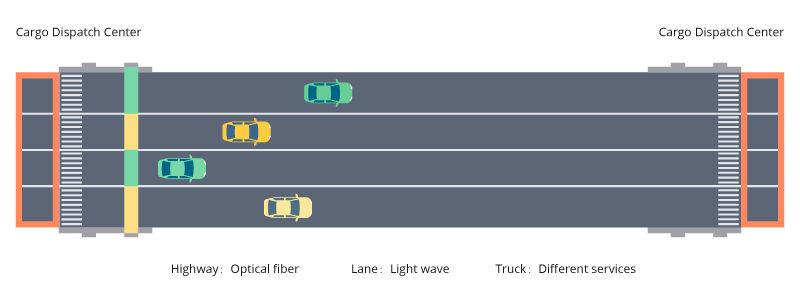
Figure5. Benefit of OTN As Cargo Dispatch Center
The advantage of the cargo dispatch center is that if the network adds new client service, it only needs to add client-side boards for accessing new services, and borrow the existing board transport service on the line side, saving network construction costs. At the same time, when a truck in a certain lane is free, it can load client service to the truck at any time through the cargo dispatch center, avoiding the waste of resources caused by the truck running empty on the lane.
Conclusion
Comparing WDM vs. OTN technology, you can find that OTN increases O&M rules by adding the frame structure to improve the monitoring, management, operation and maintenance capability of services. To sum it up, OTN is actually an optimization of WDM. Meanwhile, FS offers access networks, data center interconnect, open line systems, WDM equipments, and a variety of optical transceivers in OTN. Equipped with the most extensive and stringent testing and solution designing processes, FS provides professional and effective OTN solutions tailored to unique needs. All products undergo rigorous testing to ensure performance and quality, ensuring seamless and flexible supply to meet urgent and unpredictable global demand. FS offers 24/5 support with field engineers capable of handling the most complex issues, and all products comply fully with applicable certifications and regulations.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024













