CWDM vs DWDM: What're the Differences?
When dealing with Optical Transport Network (OTN), there are two main types of Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) systems: Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) and Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM). As two modern WDM technologies, they are both used for increasing the bandwidth of fiber by combining optical signals of different wavelengths on one strand of fiber. But CWDM vs DWDM or DWDM vs CWDM, what are their differences?
Brief Introduction to WDM, CWDM and DWDM
To better understand the difference between CWDM and DWDM, we’d better get to know what’s WDM, CWDM, and DWDM in the first place.
What’s WDM?
WDM is a technology for transporting large amounts of data between sites. It increases bandwidth by allowing different data streams to be sent simultaneously over a single optical fiber network. In this way, WDM maximizes the utilization of fiber and helps to optimize network investments.
What Are CWDM and DWDM?
As mentioned above, CWDM and DWDM are two technologies developed based on WDM, but with different wavelength patterns and applications. CWDM is a flexible technology that can be deployed on most types of fiber networks. It is typically deployed in point-to-point topology in enterprise networks and telecom access networks. While DWDM is viewed as an option for the metropolitan network. Now it is also used for interconnecting data centers and for financial services networks and is often deployed in a ring topology.
CWDM vs DWDM, What Are Their Differences?
CWDM and DWDM are both effective methods to solve the increasing bandwidth capacity of information transmission at present. But they differ from each other in many aspects. Below parts will introduce some differences between CWDM and DWDM systems.
CWDM vs DWDM: Channel Spacing
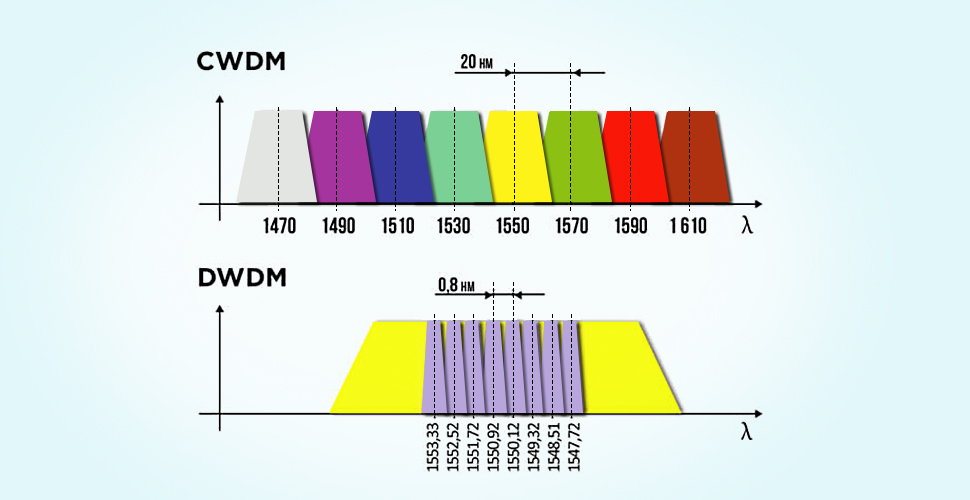
The channel spacing is defined to be the nominal difference in frequency or wavelength between two adjacent optical channels. CWDM has a wider spacing than DWDM. It is able to transport up to 18 CWDM wavelengths with a channel spacing of 20nm in the spectrum grid from 1271nm to 1611nm. DWDM can carry 40, 80, or up to 160 wavelengths with a narrower spacing of 0.8/0.4nm (100 GHz/50 GHz grid). Its wavelengths are from 1525nm to 1565nm (C band) and 1570nm to 1610nm (L band).
CWDM vs DWDM: Transmission Distance
While CWDM has a maximum reach of about 160 km and is unable to travel unlimited distances, DWDM can reach much longer distances. This is because DWDM wavelengths are highly integrated with the fiber during light transmission. An amplified DWDM system , in particular, can extend even further.
CWDM vs DWDM: Modulation Laser
CWDM system uses the uncooled laser while the DWDM system uses the cooling laser. Cooling laser adopts temperature tuning which ensures better performance, higher safety, and longer lifespan of the DWDM system. But it also consumes more power than the electronic tuning uncooled laser used by a CWDM system.
CWDM vs DWDM: Bandwidth
CWDM can carry less bandwidth per channel than DWDM. Pluggable transceivers for CWDM are now able to only reach 100 Gbps and there are integrated components that can push over 1 Tbps, whereas for CWDM the current maximum is 400 Gbps.
CWDM vs DWDM: Application
CWDM is widely used in cable TV networks and transceivers like GBIC and SFP CWDM optics, providing standardized wavelengths for efficient data transmission. Passive CWDM, ideal for FTTP, requires no power and uses passive optical components. Overall, CWDM supports cost-effective transmission of data, video, and voice signals, evolving alongside DWDM. DWDM is extensively used in telecom and cable networks for long-distance, high-bandwidth, secure applications. It's key in core and metro networks, boosting bandwidth and bringing computing closer. In high-throughput data centers, it enables service integration and supports geo-distributed architectures for data center interconnect (DCI).
CWDM vs DWDM: Cost
Because the range of temperature distribution is nonuniform in a very wide wavelength, so the temperature tuning is very difficult to realize, thus using the cooling laser technique increases the cost of the DWDM system. Furthermore, the DWDM devices are typically four or five times more expensive than that of a CWDM system. However, the price of a DWDM transceiver is about 20-25% less than a CWDM transceiver on account of the popularization of DWDM.
CWDM vs DWDM: Advantages and Disadvantages
As mentioned above, the primary difference between DWDM and CWDM is the channel spacing (CWDM has almost 100 times wider channel spacing). This makes CWDM a simpler technology, resulting in advantages and disadvantages of the different systems with regard to cost, performance, and so on.
CWDM Advantages and Disadvantages
| CWDM Advantages | CWDM Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
DWDM Advantages and Disadvantages
| DWDM Advantages | DWDM Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
CWDM vs DWDM, Which Do You Prefer?
The rising need for bandwidth has propelled DWDM's popularity due to its development and cost reduction. However, CWDM still holds a price advantage for connections below 10G and short distances, making it more feasible for lower data rates. Both CWDM and DWDM will serve distinct roles in the OTN network, complementing rather than replacing each other in the future. No matter if you opt for DWDM or CWDM, FS has a comprehensive range of products to meet your needs. Beyond offering CWDM and DWDM equipment like Mux/Demux and OADM, FS also provides an extensive selection of CWDM and DWDM modules, along with a variety of solutions tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you're seeking high-performance networking gear or customizable solutions, FS ensures that you'll find the right fit for your project within their product offerings.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024













