FS FHD® MTP® Fiber Cassettes Ideal for Modern Spine-Leaf Cabling Scenarios
As data center networks continue to grow and evolve, new challenges arise for network administrators, including the need for high-density cabling solutions that can support modern spine-leaf architecture. FS has recently launched a new line of MTP® to LC cassettes and MTP® to MTP® mesh cassettes, which are ideal for 40G to 10G, 100G to 25G, and 400G to 100G spine-leaf cabling scenarios. Then how to realize 100G to 25G connections with these two types of fiber cassettes? Find answers here.
Brief Introduction of Spine-Leaf Cabling
Spine-leaf is a network topology architecture commonly used in data centers to provide high bandwidth, low latency connections by using multiple parallel paths between the spine and leaf switches. Spine-leaf cabling applied in spine-leaf architecture typically involves using fiber optic cables to connect the spine switches to all the leaf switches forming a mesh network, and leaf switches to the servers. This design provides a highly efficient and flexible network fabric that can handle large volumes of traffic, and redundancy as traffic can be easily rerouted in the event of a switch or cable failure. However, for the high density of connections, it can be difficult to route and manage fiber cables. This is where MTP® cassettes come in.
Benefits of FS FHD® MTP® Cassettes in Spine-Leaf Cabling
FS's newly launched FHD MTP® fiber cassettes feature higher density and modular plug-and-play design, which is ideal for spine-leaf cabling. The higher density FHD® 8 x MTP®-8 mesh cassette provides eight 8-fiber MTP® ports in front and rear and can manage up to 256 fibers in a 1U rack. This mesh MTP® cassette also can reduce congestion at the MDA without breaking connections in spine-leaf cabling. And FHD® 3 x MTP®-8 to LC fiber cassettes adopt a horizontal arrangement design that the front LC adapters are corresponding to the line sequencing, which is more conforms to customer use behavior. All the new FHD® MTP® fiber optic cassettes are equipped with universal polarity used at both ends of a Method B trunk, reducing the complexity of a fiber network and streamlining network maintenance. See more about FS's new FHD® MTP® cassettes.
FS FHD® MTP® Cassettes Spine-Leaf Cabling Applications
Then how to apply MTP® fiber cassettes in spine-leaf cabling scenarios, the following shows the 100G to 25G applications of the two FS's newly-launched MTP® mesh cassette and MTP® to LC cassette.
Cross Connect with Mesh Cassette for Easier Cabling
The FHD® MTP® 8 x 8 mesh cassettes feature eight rear 8-fiber MTP® ports connections and eight 8-fiber MTP® ports in the front. This mesh cassette is connected to four individual QSFP28 100G lanes at the spine ports on one side and to the leaf switches on the other side. Every time we connect a leaf switch on the leaf side, it automatically breaks out that port into 4x4 25G lanes and shuffles them across the spine ports on the mesh cassette which are already connected to separate line cards. Therefore, the MTP® 8 x 8 mesh cassettes directly connect the QSFP28 spine switch ports and leaf switch ports without using LC connections in the main power distribution area (MDA), which lowers cabling operation costs and realizes space savings and congestion reduction.
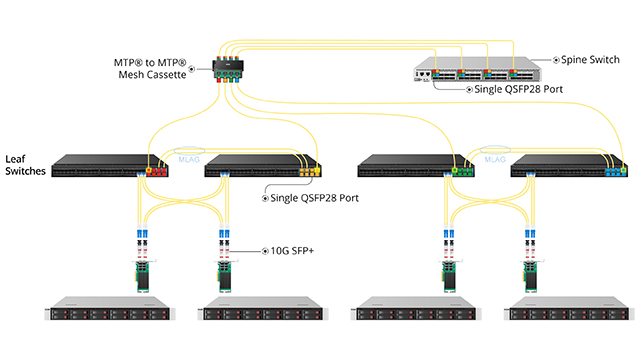
Cross Connect with Traditional Port Breakout
The FHD® series 24 fibers MTP® cassettes offer an 8-fiber MTP® adapter on the rear of the units routed to 12 duplex LC adapters on the front patch field, containing up to 96 LC fibers in 1U space, saving wiring space. All QSFP28 ports at the spine are divided into four 25G channels through the MTP® to LC cassettes. Then, we do the same exercise that uses the corresponding number of MTP® to LC cassettes to connect the 100G uplink ports of the leaf switches. Now, make an LC patch connection between the respective leaf switch and spine switch. The N*M optical fibers are fully cross-connected to maintain high redundancy and with spine-leaf architecture for eliminating latency times of east-west traffic.

You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023















