How to Choose Storage Protocol: Fiber Channel vs InfiniBand
In recent years, the application of InfiniBand and Fiber Channel in data storage has gained some attention. Enterprises have increasingly aspired to pursue high-throughput, low-latency, and higher-performance network infrastructure. What is the difference between Infiniband and Fiber Channel in network storage technology, and what is the future development trend? In this discussion, we will explore the distinctions between InfiniBand and Fiber Channel from a storage technology perspective.
Fiber Channel vs InfiniBand: What Are They?
InfiniBand and Fibre Channel differ in terms of protocol performance and application. It is important to understand their definitions and features before choosing any storage technology.
What Is Fiber Channel?
Traditional Fiber Channel networks consist of specialized hardware called Fiber Channel switches that connect storage to the SAN. Fiber Channel HBAs connect these switches to server computers. Fibre Channel (FC) is a mature storage protocol with low latency, high bandwidth, and high throughput. FC is easy to configure and manage and has been widely adopted in the past.
Fiber Channel, like InfiniBand, supports both fiber and copper media. Fiber Channel is not sensitive to noise, making it the best transmission medium. Copper media also has a variety of uses, especially for connections of small Fiber Channel disk drives. FC modules are versatile and support multiple rates to cater to different network connection requirements.
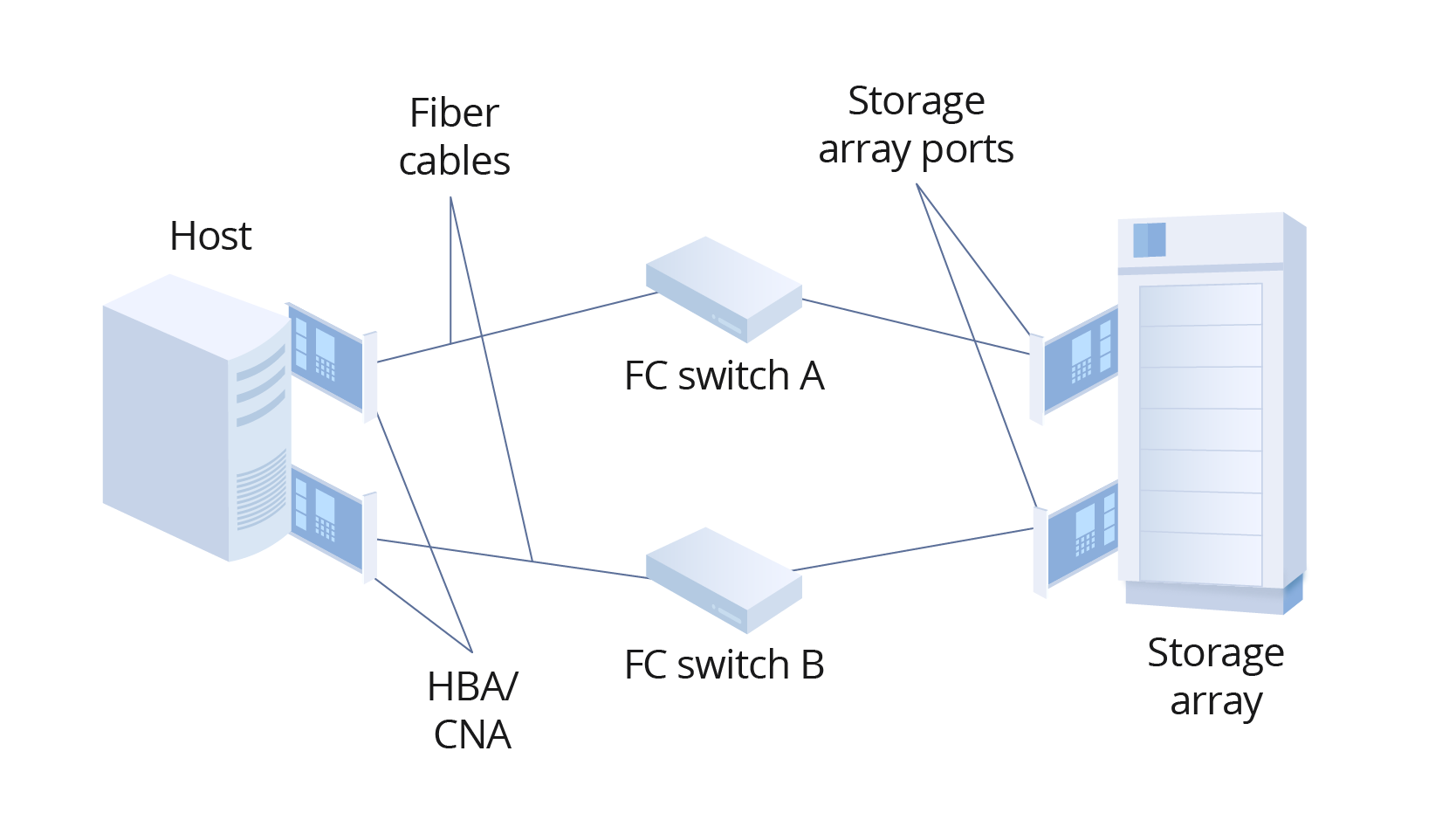
What Is InfiniBand?
InfiniBand (IB) is a modern computer network communication standard designed for High-Performance Computing (HPC). It offers low latency and high throughput, making it ideal for interconnecting supercomputers. Intel and Mellanox are the two major manufacturers of InfiniBand Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) and network switches. FS has introduced Mellanox Quantum™ chip-powered InfiniBand switches, which support 200G transmission and are among the best options available for HPC data centers.

Fiber Channel vs InfiniBand: What Are the Differences?
Compared with Fiber Channel, InfiniBand utilizes RDMA technology to achieve data transmission. It is more advantageous than Fiber Channel in HPC data centers in terms of speed, scalability, and networking methods. While Fiber Channel aims to connect thousands of devices and share data, InfiniBand is focused on communication applications.
| Contents | InfiniBand | Fiber Channel |
|---|---|---|
| Rates | 40Gb, 56Gb, 100Gb, 200Gb, 400Gb, and 800Gb | 8GFCc, 16GFC, 32GFC, and 64GFC |
| Protocol | RDMA | TCP |
| Structure | Channel-based serial transmission adopts Switched Fabric in the connection topology. | Supporting point-to-point (2 ports) and switched fabric (224 ports) topologies. |
| Scalability | Tens of thousands of nodes are supported in a single subnet, and can be expanded through routers with unlimited scale. | Start with a single switch and scale by adding more switches as needed. |
| Function | InfiniBand integrates computing engines in the network to effectively accelerate data processing for deep learning and HPC. | Fiber Channel is transparent and autonomous to the protocols mapped onto it, including SCSI, TCP/IP, ESCON, and NVMe. |
Fiber Channel vs InfiniBand: How to Choose Storage Protocol?
Based on the brief introduction, it is clear that both InfiniBand and Fibre Channel are capable of providing high-bandwidth and low-latency data transmission. However, choosing the appropriate storage protocol requires careful consideration of many factors, including performance needs, existing environment, expansion requirements, and costs.
-
Speed and Performance: The latest InfiniBand specifications support a rate of 800 Gb/s. InfiniBand typically offers higher bandwidth and lower latency, making it suitable for workloads that require large-scale data transfer and high-performance computing. The latest Fibre Channel specifications support rates of 32 Gb/s and 64 Gb/s. Fibre Channel has relatively lower bandwidth and latency, but its performance is stable.
-
Environment Compatibility: InfiniBand is typically used in newly built high-performance computing or large-scale data center environments, and it requires integration with InfiniBand hardware and technologies. However, if there are existing Fibre Channel devices, switches, and storage systems, and there are no specific requirements, Fibre Channel may be more convenient to integrate and use.
-
Scalability: InfiniBand is designed with strong scalability, supporting flexible topology layouts through the use of multiple subnets. This facilitates the easy addition, reconfiguration, or removal of subnets during system expansion or rearchitecting. Fibre Channel has high scalability in the storage domain. By adding and expanding storage devices, it can meet growing storage demands. Additionally, Fibre Channel supports multipath connections between hosts and storage devices, providing redundancy and load balancing, and supports large-scale storage systems through interconnections of Fibre Channel switches.
-
Cost: InfiniBand offers five times the performance of Fibre Channel, while being in a similar price range. Furthermore, when building a high-speed network that connects all servers and storage, using an InfiniBand fabric can eliminate the need for a Fibre Channel fabric, resulting in significant cost savings for customers.
InfiniBand Continues to Drive Forward
Both InfiniBand and Fiber Channel are capable of supporting lossless, low-latency networks and provide a degree of scalability. Compared to other storage protocols, InfiniBand switches offer superior performance with lower latency, higher data transfer rates, and larger data transfer volumes. With the rapid development of cloud computing, big data, artificial intelligence, and other technologies, InfiniBand switches will continue to drive forward and promote the advancement of high-performance computing and data transmission technology.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023















