- English
- German
- French
- Spanish
- Japanese
- Italian
- Chinese
- Chinese (traditional)
- Home
- Blog
- Case Study
- Knowledge Center
- Encyclopedia
- Story
- Video
- Blog Type
- Product
- Topic
- Region
Hot Search
- Product Updates
- Share FS
- PoE Switch
- Networking
- Networking Devices
- Home
- Blog
- Case Study
- Knowledge Center
- Encyclopedia
- Story
- Video
-
- Home
- Blog
- Case Study
- Knowledge Center
- Encyclopedia
- Story
- Video
- Blog Type
- Product
- Topic
- Region
- Home
- Blog
- Case Study
- Knowledge Center
- Encyclopedia
- Story
- Video
- English
Hot Search
- Product Updates
- Share FS
- PoE Switch
- Networking
- Networking Devices
How to View the DDM Information of Optical Transceiver via SNMP?

How to View the DDM Information of Optical Transceiver via SNMP?
Modern optical transceivers support standard Digital Diagnostics Monitoring (DDM) functions, which enable real-time monitoring of modules’ parameters. And the DDM information of the modules is commonly read via Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
The Useful DDM Function on Optical Modules
DDM is a function available on optical transceivers, including SFP, SFP+, XFP and GBIC, and is also known as digital optical monitoring (DOM). It enables users to monitor parameters of modules, such as optical output power, optical input power, temperature, laser bias current, and transceiver supply voltage, in real time. The DDM interface is defined in SFF-8472 specification published by SFF Committee. As of this writing, the latest version of SFF-8472 is Revision 12.2.
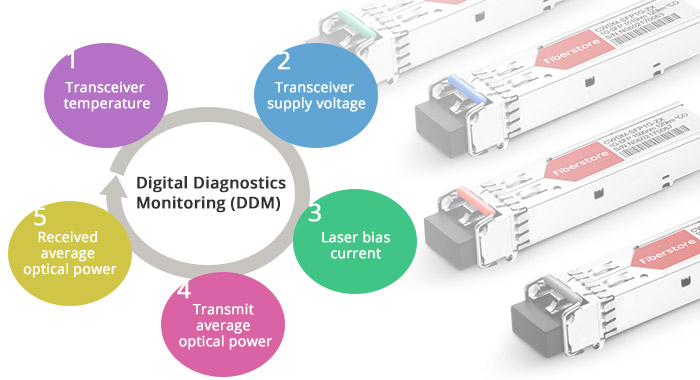 Figure 1: DDM function on fiber optic transceivers.
Figure 1: DDM function on fiber optic transceivers.
How Does DDM Work?
The DDM function works on the basis of the reference values defined in SFF-8472. SFF-8472 defines a measurement ranges, value representation and all the implementation details that are needed for both transceiver and host platform hardware and software design, so that seamless interoperability between different host platforms and transceiver vendors can be ensured. And a common set of OAM parameters, a common language, also can be shared by the whole industry. It is worth noting that the typical accuracy offered by today’s products exceeds the requirement of the document. Here are the five parameters mentioned in SFF-8472. Each of them has an individual calibration equation.
Table: Transceiver parameters defined in SFF-8472.
| Parameter | Range | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | 0~6.55V | +/-3% nominal value |
| Temperature | -128 to 128°C | +/-3°C |
| Rx power | -40 dBm to 8.2 dBm | +/-3dBm |
| Tx power | -40 dBm to 8.2 dBm | +/-3dBm |
| Laser bias | 0 mA to 131 mA | +/-10% nominal value |
DDM Offers More Than Monitoring
The DDM interface allows real time access to device operating parameters, and it includes a system of alarm and warning flags which alerts the host system when particular operating parameters are outside of a factory set normal operating range. For example, if the transceiver temperature that follows SFF-8472 exceeds the threshold level, the peculiar bit belonging to the temperature will be stated in the memory map of the device, then the platform supervision system can quickly check if the interface is working correctly by polling the status registers.
In addition to real-time monitoring, DDM function is also able to be used for fault prediction. Generally, the output power of a normal optical module will be controlled at a stable level, which is achieved by increasing the bias current of the laser (Tx_Bias). But with the operating time of the laser increased, the quantum efficiency of the laser is reduced. Therefore, users can monitor the laser's bias current to predict the laser's life. This prediction enables network managers to find potential link failures before system performance is affected. With the predicted notice, system administrator can start the backup link and repair the systems without interruption.
Besides, the DDM function can be used to isolate the particular location of fault in fiber optic network system. Combining the DDM interface status flags, transceiver hard pins and diagnostic parametric monitor data, the specific location and cause of a link failure can be pinpointed.
How to View the DDM Information Via SNMP?
As mentioned in the abstract, DDM information of optical transceivers are commonly viewed via SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). Before going to how to use SNMP, let’s first get familiar with SNMP itself and its related components.
An Overview on SNMP, MIB and OID
SNMP is a technology used in network monitoring. It consists of three key components: managed devices, agents, and network-management systems (NMSs). A managed device is a network node that has an SNMP agent and resides on a managed network. These devices can be routers and access servers, switches and bridges, hubs, computer hosts, or printers. An agent is a software which runs on managed device. This agent translates information into a compatible format with SNMP. An NMS runs monitoring applications. They provide the bulk of processing and memory resources required for network management.
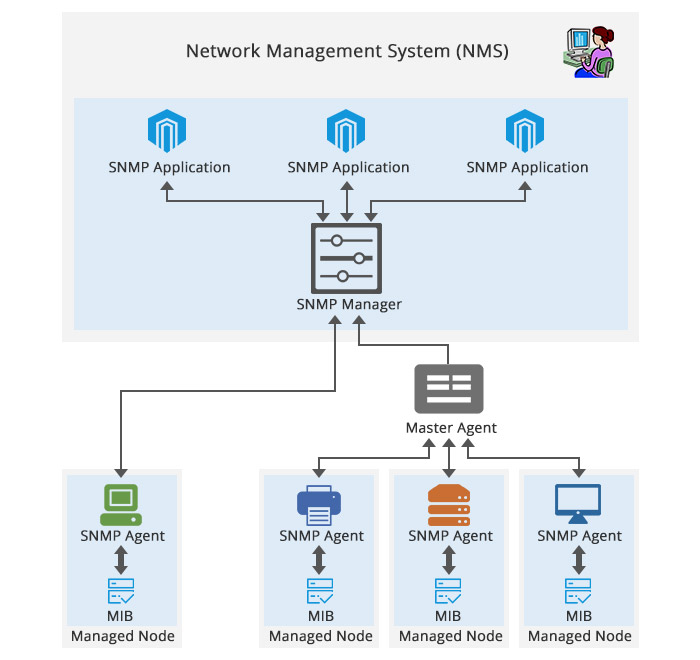 Figure 2: SNMP basic architecture.
Figure 2: SNMP basic architecture.
MIB (Management Information Base) is a collection of information which is organized hierarchically. The various pieces of information are accessed by a protocol such as SNMP. For example, on a switch the typical objects of interest are the incoming and outgoing traffic as well as the rate of package loss or the number of packets addressed to a broadcast address. Each vendor of SNMP equipment has their own section of MIB tree structure at their disposition, e.g. CISCO-ENTITY-SENSOR-MIB.
OIDs (Object Identifiers) uniquely identify managed objects in an MIB hierarchy. It can be depicted as a tree whose nodes are assigned by different organizations. Generally, an OID is a long sequence of numbers, coding the nodes, separated by dots. OIDs are generally provided by the hardware manufacturers or can be found in so-called OID repositories, where collections of MIB trees and the corresponding OIDs can be accessed.
Monitor the Optical Transceiver Parameters via SNMP
The parameters of optical transceivers can be monitored via SNMP, on the premise that your transceiver does support DDM. After enabling the DDM function of transceivers, the Net-SNMP (snmpwalk) tool is typically used to poll the information.
Sample for Net-SNMP tool: Take the Cisco ASR9k as example. We want to read the optical Tx/Rx power of the module via SNMP. The ASR9k is IOS-XR, Version 5.3.1. The MIB is “CISCO-ENTITY-SENSOR-MIB” and the OID is 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.91.1.1.1.1. So the command by using Net-SNMP tool is like:
 Figure 3: Sample for snmpwalk command.
Figure 3: Sample for snmpwalk command.
Then the CLI will show the output of celsius/amperes/mWatts/voltsDC sensors, and you just have index to the particular sensor you need.
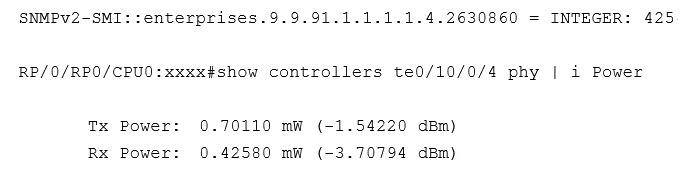 Figure 4: Transceiver power output.
Figure 4: Transceiver power output.
Note: Ensure the Package Installation Envelopes (PIE) are loaded before polling. The optical power will not be presented as “dBm” but as “mW”. To convert mWatts to dBm with the formula 10*log(mW) = dBm.
Since there are different SNMP equipment vendors, there will be some difference in MIB and OIDs. And some devices are able to show the DDM information by only using some simple command like show optic port-number to get the result of single transceiver:
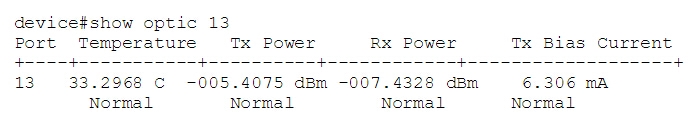 Figure 5: Show optic command result. (source: Brocade)
Figure 5: Show optic command result. (source: Brocade)
or by using show optic slot slot-number to get all optics in a particular slot.
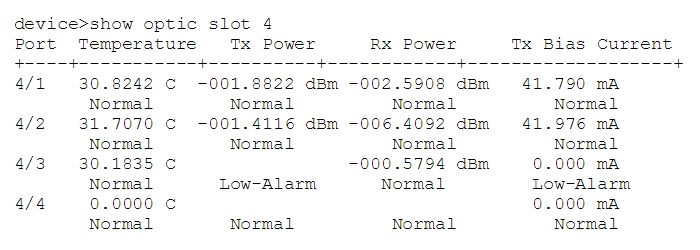 Figure 6: Show optic slot command result. (source: Brocade)
Figure 6: Show optic slot command result. (source: Brocade)
Expecting More on Optical Transceiver Monitoring?
After knowing the DDM function, most of us might have questions about monitoring transceivers except those covered by the SFF-8472 document. Though the DDM interface is only applicable to SFP, SFP+ and GBIC optical modules, the DOM function is available on many QSFP and CFP transceiver modules. So it will be possible to monitor these transceivers’ metrics as well. And since not all fiber optic transceivers support DDM/DOM, before trying to learn about the optical parameters through SNMP, it is necessary to check whether it supports the function or not. Otherwise, all the efforts will be in vain.
Key Acronyms:
DDMI = Digital diagnostics monitoring interface
SFP = Small form-factor pluggable
SFP+ = Small form-factor pluggable plus
XFP = 10 Gigabit small form-factor pluggable
GBIC = Gigabit interface converter
MSA = Multisource Agreement
SFF Committee = Small form factor committee
OAM = Operation Administration and Management
SNMP = Simple Network Management Protocol
MIB = Management Information Base
OID = Object Identifier
CLI = Command Line Interface
PIE = Package Installation Envelopes, are nonbootable files that contain a single package or a set of packages
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023














