Media Converter vs Ethernet Extender: How to Choose?
Copper-based Ethernet transmission has a distance limitation of merely 100 meters, which inevitably impedes the growing demands of higher bandwidths and longer transmission distances. Using media converter and Ethernet extender are both feasible solutions for dealing with this challenge, but what are the differences between media converter and Ethernet extender and when to use media converter or Ethernet extender?
Media Converter vs Ethernet Extender Overviews
Media converter is a cost-effective device mainly used for copper-to-fiber conversion or fiber-to-fiber connections for extending transmission distances and improving transmission quality. Fiber media converter adds fiber cabling to the legacy copper cabling system, therefore extending the service life of original facilities and bringing new technologies and applications available for network upgrades.
While Ethernet extender converts Ethernet to DSL (Digital Simulation Language) and reverts signals back to Ethernet, which helps extend 10/100/1000 Ethernet connection using coaxial cabling, copper wiring or single twisted pair such as Cat 5e/6/7 that primarily deployed in alarm circuits, T1/E1 circuits, RS-232, RS-422, RS-485, CCTV (Closed Circuit Television) and CATV (Community Antenna Television) applications. It eliminates the need for installing a new cable infrastructure, saving costs and time.

Figure 1: Media Converter vs Ethernet Extender.
Media Converter vs Ethernet Extender: Which to Choose?
With compact size and independent power supply, media converter and Ethernet extenders can be both flexibly installed for LAN extension. But distinct differences can also be found between media converter and Ethernet extender.
Media Converter vs Ethernet Extender Performances
Their performances are quite different. Media converter usually performs the function of photoelectric conversion. In copper-to-fiber connections, a pair of media converters are used to convert electrical signals to optical ones and vice versa. In fiber-to-fiber connections, media converters bridge multimode to single-mode fiber, dual fiber to single fiber or achieve wavelength conversion. While Ethernet extender converts Ethernet to DSL and reverts signals back to electrical format across coax cabling, T1/E1 and copper cabling. And their transmission efficiency largely depends on the physical media used. Thus, media converters can support 10/100/1000Mbps or even 10Gbps, reaching longer transmission distance up to 160 km. While extender usually supports Ethernet speeds of 10/100/1000Mbps, allowing 10/100Base-TX Ethernet data with SHDSL technology to be transmitted up to 20 km or extending 10/100/1000Base-T Ethernet up to 3 km using VDSL technology.
When to Use Media Converter or Ethernet Extender?
Media converters are commonly used in all sorts of industries and sectors to provide a connection between fiber and copper, such as enterprises, campus and Metro Ethernet. The figure below illustrates a typical application case of fiber optic media converter - it is used to connect telecommunication room switch to workstations located beyond 100m in a large facility. The Ethernet switch is connected to the media converters on the chassis via copper cable. Each end device, such as a workstation, is also linked to the media converter for converting UTP signal to optical signal, which is then sent back to the computer room.
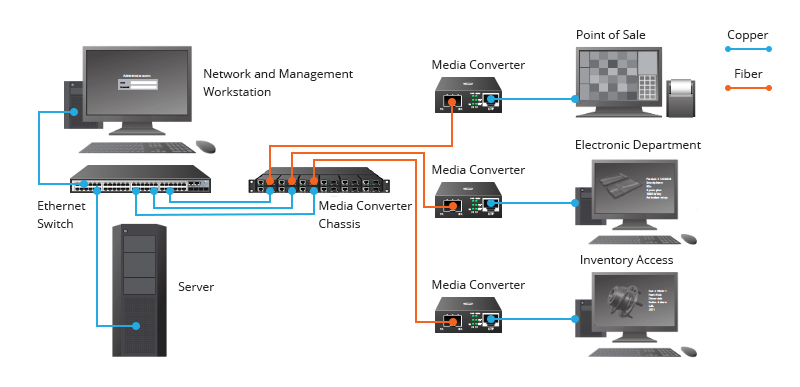
Figure 2: Application of Media Converter.
There are also cases when you have to use original facilities to extend your LAN. If there is an existing twisted-pair copper or telephone wire running, then using a pair of Ethernet extenders can be the best fit. Extenders will work with all sorts of copper wire already in place, significantly cutting down the labor and cabling involved in a network installation. As shown in the following picture, the Ethernet extenders are deployed to connect the main office to Manufacturing Plant A, B, C respectively by converting Ethernet to UTP, so as to extend transmission distances.
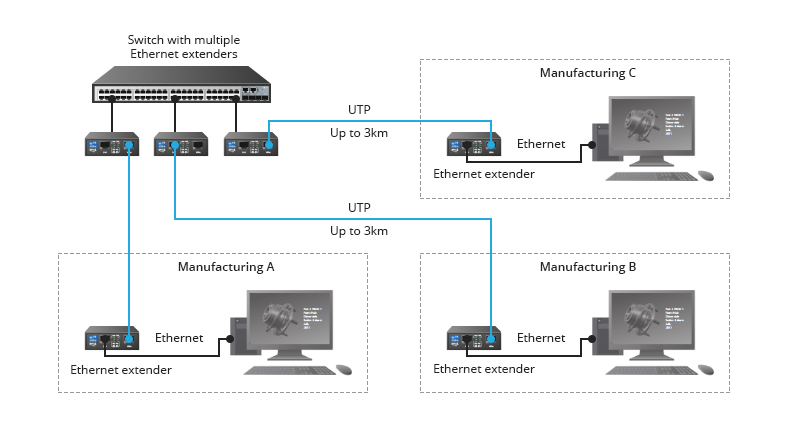
Figure 3: Application of Ethernet Extender.
Conclusion
Media converter vs Ethernet extender differences come in many aspects. Although the two devices can be both used to extend LAN using the existing cabling system, media converter usually performs photoelectric conversion using fiber cables while Ethernet extender deals with electrical signals and DSL together with twisted pair or coaxial cables. Fiber media converter enables the best performance for long-range network extension but is also cost-prohibitive. So one should better consider the real situation and make a viable choice between media converter and Ethernet extender.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023














