Network & Communication Cables That Power Your Internet
Quick Guide to Major Types of Network Cables Specifications.
Network cables are often applied for connecting one network device to another, which cover twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, power line, etc. The first three network cable types are categories that are most often referred to. The following description will introduce the basic information, specification and application of these network cables.

Twisted Pair Network Cable Types & Specifications
A twisted pair network cable is a type of wiring in which two conductors (usually copper) of a single circuit are twisted together. By twisting two insulated copper wires together at a certain density, the electric waves radiated by each wire in transmission will be offset by the electric waves emitted from the other wire, effectively reducing the degree of signal interference. Twisted pair cabling is often used in data networks for short and medium-length connections because of its relatively lower costs compared to optical fiber and coaxial cable.
Twisted Pair Network Cable Types & Standards
According to the frequency and signal-to-noise ratio, the twisted pair network cable can be divided into Cat 3, Cat 4, Cat 5, Cat 5e, Cat 6, Cat 6a, Cat 7, Cat 7a and Cat 8 Ethernet/copper cables. Cat is standard for Category, all of them are applied for short distance transmission. The detailed specifications of twisted pair network cable types are listed in the below chart.
| Category | Typical Construction | Max Bandwidth | Transmission Speeds | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat 3 | UTP | 16 MHz | 10Mbps | 10BASE-T and 100BASE-T4 Ethernet |
| Cat 4 | UTP | 20 MHz | 16Mbps | 16Mbit/s Token Ring |
| Cat 5 | UTP | 100 MHz | 10-100Mbps | 100BASE-TX & 1000BASE-T Ethernet |
| Cat 5e | UTP | 100 MHz | 1000Mbps-1Gbps | 100BASE-TX & 1000BASE-T Ethernet |
| Cat 6 | STP | 250 MHz | 10Gbps (55m) | 10GBASE-T Ethernet |
| Cat 6a | STP | 500 MHz | 10Gbps (55m) | 10GBASE-T Ethernet |
| Cat 7 | STP | 600 MHz | 100Gbps (15m) | 10GBASE-T Ethernet or POTS/CATV/1000BASE-T over single cable |
| Cat 7a | STP | 1000 MHz | 100Gbps (15m) | 10GBASE-T Ethernet or POTS/CATV/1000BASE-T over single cable |
| Cat 7a | STP | 2000 MHz | 4Gbps (30m) | 40GBASE-T Ethernet or POTS/CATV/1000BASE-T over single cable |
Note: For more specific information on how to buy a right copper cable, please refer to Best Ethernet Cable Buying Guide.
T568A and T568B are two basic wiring standards that are used by twisted pair network cables. They are telecommunications standards from TIA and EIA that specify the pin arrangements for connectors (often RJ45) on UTP or STP network cables. The number 568 refers to the order in which wires within the twisted pair cables are terminated and attached to the connector. The only difference between T568A and T568B is that the orange and green pairs are interchanged (see the figure below).

Shielded or Unshielded Twisted Pair Network Cable?
Shielded and unshielded twisted pair cables are often recognized as the common twisted pair network cable types in networking solution, which can be described as STP and UTP twisted pair cable respectively.

The UTP refers to the cable that lacks metallic shielding around copper wires, which can help minimize electronic interference by providing balanced signal transmission. Thus it is mostly used in short-distance transmission for indoor telephone applications, computer networks, and even in video applications.
As for STP cable, the wires are enclosed in a shield that functions as a grounding mechanism to provide greater protection from electromagnetic interference and radio Infrequency interference, allowing it to carry data at a faster rate of speed. Therefore, STP twisted pair network cable is often used in high-end applications that require high bandwidth and outdoor environments.
What Is Coaxial Network Cable?
Coaxial cable is a type of network cable that has an inner conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The inner conductor and the outer shield share a geometric axis. Many coaxial cables have an insulating outer sheath or jacket.
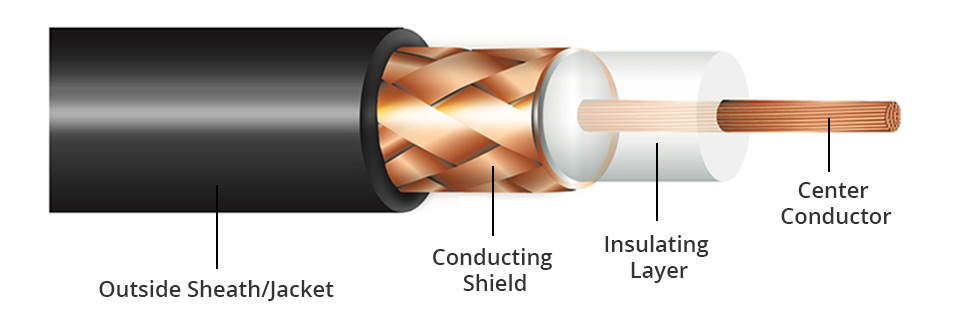
Coaxial cable is used as a transmission line for radio frequency (RF) signals. Its applications include feedlines connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas, computer network connections, digital audio, and distributing cable television signals. Coaxial cable has an obvious advantage over other types of radio transmission line. In a good coaxial cable, the electromagnetic field carrying the signal exists only in the space between the inner conductor and the outer conducting shield. For this reason, coaxial cables are allowed to be installed next to metal objects without power losses that occur in other types of radio transmission line.
What Is Fiber Optic Cable?
Optical fiber cabling is an excellent transmission medium for its high data capacity and supported long distances. It has a fiber/glass core within a rubber outer coating and uses beams of light rather than electrical signals to relay data. The fiber optic cables can run for distances measured in kilometers with transmission speeds from 10 Mbps up to 100 Gbps or higher due to the fact that light doesn't diminish over distance the way electrical signals do.

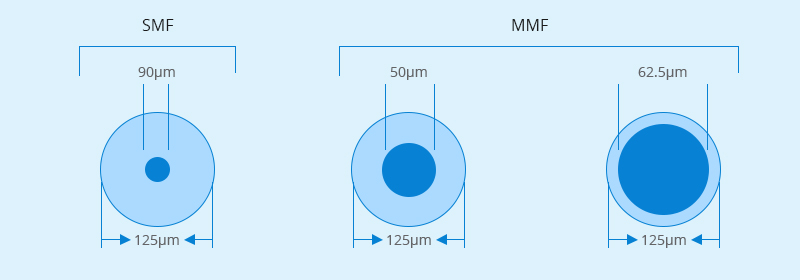
Generally, fiber optic cable consists of single mode and multimode fibers, the difference is the core diameter. The former fiber core is 9/125µm wide and the latter fiber core can be 62.5/125µm or 50/125µm wide. Both multimode fiber (MMF) and single mode fiber (SMF) can be used for high-speed transmission. MMF is often for short reach while SMF is for long reach.
Conclusion
Twisted pair, coaxial cables and fiber optic cable are three major network cable types in the communication systems. They have different cable structions, speed, bandwidth, and applications. All of them will benefit both in our daily life and in network construction work. For more detailed differences, please check it here: Fiber Optic Cable vs Twisted Pair Cable vs Coaxial Cable.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023














