QinQ vs VLAN vs VXLAN: A Comprehensive Introduction of Switch Functions
Overview of VLAN, VXLAN and QinQ
VLAN
VLAN is a technology to segment network into several broadcast domains. In each broadcast domain, users can communicate with each other freely. As for connections between different VLANs, VLAN tagging and inter-VLAN routing are two necessary terms that users must know. VLAN tagging is to add a special tag into the frame when it passes through the VLAN trunk port which allows frames from different VLANs to cross. And one of its VLAN tagging methods is IEEE 802.1Q. In CLI and Web user interface of switches, VLAN configuration is simple and easy. The following video shows VLAN configuration via CLI (command-line interface) and Web user interface on FS S5800 series, S5850 series and S8050 series network switches. More about VLAN, you can read this artical:What Is Private VLAN and How It Works?
QinQ
QinQ, also known as VLAN stacking or double VLAN, is standardized by IEEE 802.1ad. It encapsulated the VLAN tag with two layers (double tagging)—an inner tag of a private network and an outer tag of the public network. As there are increasing users in networks, which require large numbers of VLAN ID. The traditional VLAN tagging that uses IEEE 802.1Q is unable to identify and isolate users’ data on expanding metro Ethernet works. Therefore, QinQ is used to extend the VLAN numbers up to 4096×4096, which can save public VLAN IDs effectively.
There are two kinds of QinQ implementations, basic QinQ and selective QinQ. Basic QinQ is a tagging method based on port which will default tag all packets. Selective QinQ can identify the inner VLAN tag according to the MAC address, IP protocol, etc., and then determine which tag it should be added.
VXLAN
VXLAN, also called virtual extensible LAN , is designed to provide layer 2 overlay networks on top of a layer 3 network by using MAC address-in-user datagram protocol (MAC-in-UDP) encapsulation. In simple terms, VXLAN switches can offer the same services as VLAN switches does, but with greater network scalability and flexibility. If you have relevant requirements, these 10G enterprise switches from FS can all support VXLAN. Similar to QinQ, VXLAN have a relatively fixed packet format too. With VXLAN MAC-in-UDP encapsulation, the original packets will be added on a VXLAN header and then placed in an UDP-IP packet.
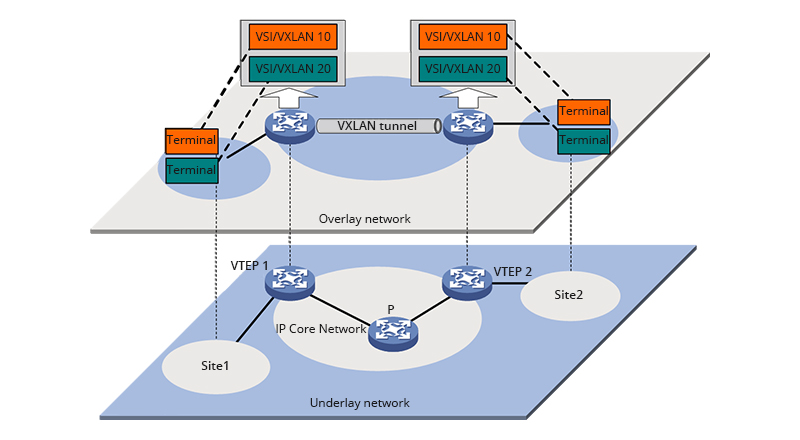
The Differences Between QinQ, VLAN and VXLAN
VLANs have been used to solve different problems like Layer 2 network isolation, flood and as routing interface. VLAN configuration is now available in most systems and network equipment such as Ethernet switches, routers and firewalls. However, the following comparison mainly focuses on VLAN tagging. To realize communication between different VLANs in networking, VLAN tagging is an essential part.
QinQ vs VLAN
As has mentioned above, VLAN tagging uses the network protocol IEEE 802.1Q or ISL (Inter-Switch Link) to tag frames flowing through different VLANs. Frames that are tagged with this method have only one tag. However, QinQ VLAN switches is more flexible than VLAN switches. On one hand, it can add tags to the incoming frames or packets selectively. On the other hand, the outer VLAN tag solves the problem of limited VLAN IDs. And the unique inner tag avoids conflict between the private VLAN IDs and the public VLAN IDs, providing a simple layer 2 VPN solution for small-scale or large enterprise networks.

VXLAN vs VLAN and QinQ
When it comes to VXLAN, it offers the same functions as QinQ in some degree, but its working layer is more extensible. VXLAN encapsulates packets by MAC-in-UDP, extending layer 2 networks greatly. As we know, with the advancement of cloud computing, tenants have more demanding requirements for network builds, especially for the virtualized data center, which enhances the need for layer 2 networks. MAC-in-UDP supports the use of 24-bit VINDs, which allows a data center to accommodate multiple tenants, breaking the physical distance and deployment restriction. That’s why VXLAN is becoming more popular in cloud computing and virtualized data center in recent years. However, compare to VLAN and QinQ, VXLAN technology is more expensive and complicated. Therefore, not all VLAN switches support this function. FS.com N series data center switches like N5860-48SC and N8560-48BC support VXLAN and other data center features, which are designed to offered high performance for layer 2/3 networks.
Conclusion
With the increasing demand of network scalability, and the fast development of VLAN technology and layer 2/3 networks, more higher network management technologies will arise definitely. Like the QinQ and VXLAN technologies of switches, not all technologies are created equally. All of these switch configurations are born to solve network management problems at present, and will bring more convenience for future networks.
Related resource: VLAN: How Does It Change Your Network Management?
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023















