Unveil the Myths About SDN Switch
Virtualization has become an irresistible trend in data center networks and enterprise networks. It makes the network more agile and flexible with the ability to abstract vast amounts of resources and manage multiple environments from one single controller. Software-defined networking (SDN) is one of the key technologies that make it real. Vendors and manufacturers release new products that can be used in SDN environments in succession, which include one of the key components — SDN switch. What is an SDN switch? Is it more complicated than normal Ethernet switches?
What Is SDN Switch?
An SDN switch is a software program or hardware device that forwards packets in an SDN environment. It must support SDN protocols. The earliest as well as the most commonly known SDN protocol is OpenFlow. Therefore, an SDN switch is often called OpenFlow switch as well. There are also some other SDN protocols that are developed by SDN switch vendors, such as OpFlex, NETCONF, BGP (Border Gateway Protocol), XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol), etc.
Using the earliest protocol defined in the SDN environment, OpenFlow switch has evolved from OpenFlow v1.0. in 2011. OpenFlow v1.5.1 is the latest OpenFlow version that has support from switch vendors.
How Does an SDN Switch Work?
Whether it is a virtual (hypervisor-based) switch or a physical switch, an SDN switch only keeps the data plane (packet forwarding) in itself. The control plane (high-level routing) is decoupled from the SDN switch hardware but implemented in the SDN controller (an application running on the server or somewhere), which lies between network devices and applications. Every SDN switch in the SDN model is programmable by the SDN controller through SDN protocols. And communications between applications and devices are achieved by going through the SDN controller.
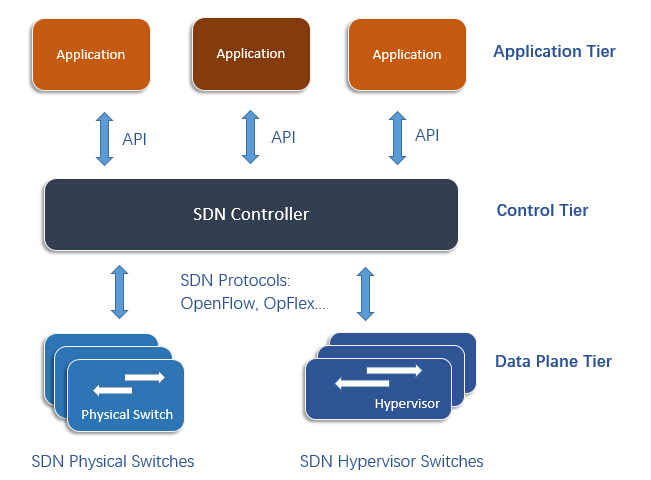
An SDN switch consists of ports and tables. Packets arrive and leave the switch through ports. Tables consist of rows containing a classifier and set of actions. When an SDN switch receives a packet which does not have a match row in the table, it will communicate with the SDN controller and ask what to do with this packet. The controller can download a flow to the switch, which includes the first classifier that best matches the packet and the actions. Actions administer the treatment of the packet, which can be forwarding it to the port(s), encapsulating and forwarding it to the controller, dropping the packet, or sending it to the normal processing pipeline. Once the flow is downloaded to the switch table, it will switch similar packets at wire speed. This automated process makes it easier to integrate and manage different applications.
Benefits of Adopting SDN Switch
There are mainly two benefits of adopting SDN switches:
Easier Flow Control and Configuration
With SDN switches, you do not need to go to the locations of the switch and login to the command line to configure it. You can remotely control and program multiple switches through one single SDN controller that uses SDN protocol and provides API (Application Program Interface) for SDN switches.
Easier to Do Load-Balancing
Other benefits are that it will be easier to do load-balancing even at high data rates, and the traffic can be isolated without the need for VLANs, since the SDN controller functions to refuse certain connections.
Can a Conventional Switch Work as SDN Switch?
Some users have had many early-stage switches in use that are non-SDN switches but still want to enjoy the benefits of SDN environment. So they may ask if their “old” switch can be used as SDN switch. In fact, there has been experimentation on bringing early-stage switches into use in SDN environment. One possible approach is to use Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM) with OpenFlow v1.0. By using TCAM, early hardware vendors can insert a flow from an SDN controller into the switch forwarding table for subsequent flow lookups of a flow. But TCAM is not the most efficient recipe for switch hardware search lookups, because it is power hungry, expensive and takes up quite a bit of silicon space. There might be some better ways to retro-fit the conventional switches to accommodate the SDN environment in the future.
Conclusion
In the SDN environment, network performance has become more delightful and network management has become more convenient in data centers and enterprises, of which SDN switch is one typical product of this technology. SDN switches using protocols like OpenFlow well meet the requirements of network virtualization in an open networking environment. Its wide deployment in different network infrastructures is not hard to see in the foreseeable future.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023














