Upgrading Your Data Center to 100G Ethernet
The rise of video streaming and the significant increase of IoT devices lead to the explosive growth of data. To handle massive data and support various cloud-based services, data centers are being built globally. Apart from the increase in volume, data centers also require upgrades and migration to 100G and beyond to provide high-performance computing, storage, and content delivery services to enterprise and customer users.
Time for 100G Ethernet
Due to more cloud-based services, new network technologies, and massive network densification such as the exponential growth of wireless devices, networks are becoming more complex. Besides improving server CPU performance, server density and virtualization have increased to handle dramatically increasing data in modern complex networks, which accelerates uplink speeds for switches. These factors drive the need for faster interconnects and data center throughput speeds.
While many organizations still rely on 10G and 40G, many giant corporations, such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft, have been deploying 100G Ethernet in their data centers since the development of 100G. Many operators of large-scale data centers are also gradually increasing the transmission speed of their Ethernet networks. The implementation of 100G enables data centers to gain operational efficiency and a more scalable environment to accommodate increasing densities and rapid growth.
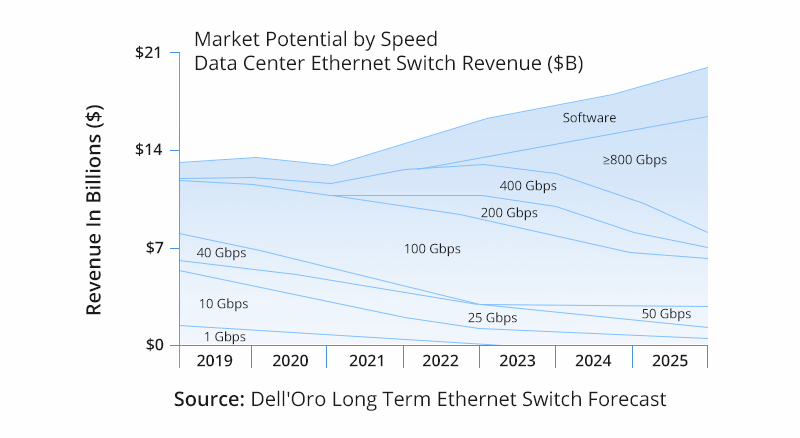
The 100G era has arrived. At present, 100G switch ports and 100G optical devices are ubiquitous in data centers. According to Dell'Oro forecast, in the future, even if 800G (2×400G or 8×100G) will develop rapidly, 100G devices will still occupy a large market share. Therefore, the migration to 100G is the dominant trend in today's data centers.
Planing Data Center Upgrades to 100G Ethernet
To improve overall performance, organizations should evaluate the current state of their data center and plan for upgrades to 100G Ethernet. Here are three considerations for data center upgrades.
Physical Infrastructure Upgrade for 100G Data Center
As data center speeds increase, the performance of the physical infrastructure becomes increasingly important for link quality.
Multimode optics (multimode transceivers and multimode fibers) is widely used for 10G and 40G (4×10G) Ethernet deployment in data centers, which can satisfy most data center reach requirements. However, for 25G and 100G (4×25G) Ethernet deployments, QSFP28 transceivers are the most popular solution that can connect to Ethernet switches with 100G ports.
With its high density and low power consumption, the 100G QSFP28 is an ideal optical module solution for large-scale 100G data centers as it can meet current network requirements while preparing for future network expansion.
Multimode Fiber and Singlemode Fiber
It's recognized that optical networking equipment can achieve higher bandwidths to support growing application demands. Many enterprises are deploying 40G and higher speeds in their data centers through multimode fiber (MMF) or single-mode fiber (SMF) cabling.
Multimode solutions dominate in applications with distances less than 100m. Multimode fiber (MMF) link distances are limited by transceiver link loss budgets as well as modal and chromatic dispersion. It primarily meets the need for in-building connectivity. 10G/40G data center cabling system mostly adopts OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers. For data center upgrades, OM5 multimode fiber is more suitable for 40G/100G high-speed Ethernet link transmission due to its better performance and high scalability.
SMF cables can carry large amounts of data over long distances with low power loss. It is preferred for data centers requiring higher speed and longer network distance. To be more specific, if you are at 10G and trying to migrate to 100G data centers, with many links longer than 100m, you need to upgrade your cables to single-mode fiber.
Prepare for the Evolution of Data Center Technology
There's no sign that network demand will slow down, so 100G is really just a stepping stone toward faster connectivity. Hyperscale data center operators and service providers are already implementing 400G connectivity in their data centers. Speeds of data center links are ratcheting up to 400G in the core and spine, 200/400G in the leaf, and 50/100G in top-of-rack architectures, as shown below.

To support long-term data center development, enterprises need to choose future-proof 100G devices, such as 100G QSFP28 and 100G CFP. 100G QSFP28 is mostly used in shorter distances (0-10km) between switches, and CFP is suitable for metropolitan area networks (MANs) and long-haul WDM transmissions.
The Closing Thought
The migration from 10G/40G to 100G is an inevitable trend for data centers. 100G optical modules and fiber deployments are helping hyperscale data centers meet unprecedented data demands. When planning 100G data centers, physical infrastructure upgrades are essential. In order to select the most appropriate upgrade solution, enterprises also need to take performance, cost, loss budgets, distance, and other features into consideration.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023















