Complete Guide to Software-Defined Data Center
With the booming development of technologies such as software-defined computing, storage, and networking, the software-defined data center (SDDC) has emerged and becomes an important concept in next-generation data centers. It eliminates the IT operational complexities and accelerates IT service delivery through virtualization, showing high availability. This article will take you through software-defined data centers in detail to help you determine whether to adopt SDDC.
What Is a Software-Defined Data Center?
A software-defined data center refers to a data center that virtualizes its infrastructure by abstracting, pooling, and automating IT resources. SDDC leverages software-driven tools to centrally manage these virtualized resources and automate operations and workflows. The core resources of SDDC are compute, storage, and network. Nowadays, many organizations, such as cloud service providers and data center service providers, regard software-defined data centers as the next-generation data center and start adopting SDDC at scale.
SDDC Architecture
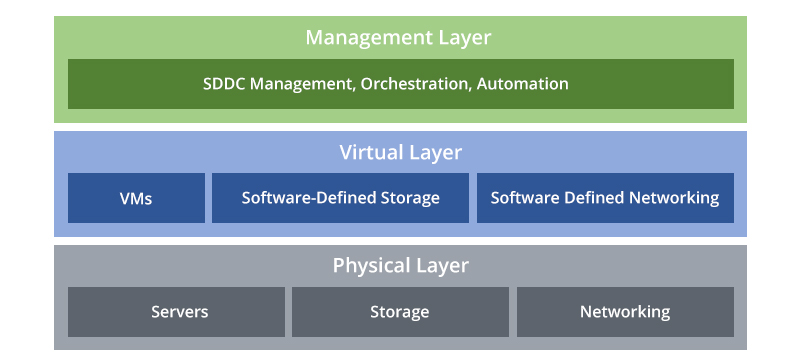
SDDC architecture shows a complex approach to data center management, and it has multiple layers focusing on different functions.
The physical layer is the actual hardware—the compute, storage, and network devices in the data center. This layer focuses on the performance and functional stability of the devices, providing a stable environment for SDDC's entire network and business operations.
The virtual layer controls access to the underlying physical infrastructure and abstracts resources to deliver them as services. It's responsible for network operation monitoring and resource allocation, simplifying data center management and improving efficiency.
The management layer standardizes management and enables orchestration and automation capabilities, which allows SDDC to be controlled from a centralized interface.
The Core Components of SDDC
Virtualization technologies are the key that software-defined data centers use to abstract, pool, manage, and deploy data center functions, and are core components of SDDC. SDDC is made up of four architectural components: compute virtualization, storage virtualization, network virtualization, automation, orchestration, and management, allowing organizations to efficiently allocate and manage their IT resources.

Compute Virtualization
Compute virtualization, also called server virtualization, abstracts server resources, including their operating systems, CPUs, memory, and software, from physical servers. As a result, administrators can use virtualization software, called a hypervisor, to organize and manage the computer's virtualized resources, and use virtual machines (VMs) to handle multiple workloads simultaneously.
Storage Virtualization
Storage virtualization pools resources and are responsible for provisioning and managing data storage from the pool. With storage virtualization, organizations often do not need to purchase new capacity and can dynamically allocate those resources to provide the required capacity for each application as needed.
Network Virtualization
Network virtualization is used to provision the network infrastructures serving virtual machines, independently of the underlying physical hardware. It allows administrators to respond quickly to changing business requirements without physical constraints.
Automation, Orchestration, and Management
Automation refers to automating a single process such as deploying a virtual server. Orchestration refers to automated configuration, management, and coordination of computer systems, applications, and services. Software-defined data centers use management and automation software to keep business-critical functions working continuously.
The Benefits of a Software-Defined Data Center
Based on its unique features, a software-defined data center allows organizations to obtain more flexible and rapid business deployment, management, and implementation at a lower cost.
Improve Business Agility
With infrastructure management, automation, and service orchestration functions, SDDC eliminates physical hardware dependency and enables resource provisioning in real time, which can handle dynamic workloads and respond quickly to fluctuating business demands. To be more specific, the time to deploy and provision resources can be significantly reduced. And it no longer takes a long time to provide more storage capacity for applications and modify physical networking.
Increased Scalability
SDDC enables the dynamic scalability of resources based on business needs. The cloud-based SDDC allows organizations to scale up or down functionality as needed to meet changing demand. Increasing or decreasing IT resources, such as data storage capacity, processing power, and networking, is pretty simple. SDDC offers unlimited scalability. There is no need to worry about freeing up more space to meet growing business needs.
Cost Efficiency
An SDDC can help reduce costs. Traditional data centers require additional IT manpower, expensive equipment, time, and maintenance. While, software-defined data centers can avoid large capital expenditures. For example, SDDC pools resources, which improves infrastructure utilization and reduces the costs of new infrastructure purchases. Better utilization also means reduced expenses of electricity, cooling, etc.
Simplified Data Center Management
SDDC can be managed through a central dashboard, allowing IT users to monitor data, update systems, and allocate additional storage resources. Compared to traditional data centers, which may require multiple IT tools, applications, and software to manage, SDDCs make data center management much simpler.
Why Uses Software-Defined Data Center
There are obvious limitations of traditional data centers, such as high input costs, lack of efficiency, and difficulty in management. It is labor-intensive to operate and maintain, and adding new resources can be time-consuming. Expanding these data centers can also be quite difficult.
However, SDDC offers a great deal of flexibility and agility in enterprises' business processes. Moreover, it makes it easier to manage and scale data centers and allows for better control and management of resources, improving the efficiency and utilization of IT resources. Therefore, software-defined data centers are adopted by many IT organizations, infrastructure and operations leaders.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024














