EVPN-VXLAN: How to Use It in Data Center
The rapidly increasing use of mobile devices, social media, and collaboration tools is adding more and more endpoints to the network. The proliferation of endpoints drives a need for more effective segmentation strategies to separate different profiles of users, devices, and traffic. EVPN-VXLAN establishes tunnels of Layer 2 overlay virtual networks through a physical Layer 3 underlay network, providing enhanced flexibility for endpoint management. As a result, it has emerged as a widely-deployed networking framework.
What Is EVPN-VXLAN?
EVPN-VXLAN refers to a network architecture that stretches Layer 2 connections over a Layer 3 underlay network, forming network overlay. EVPN-VXLAN is the combination of EVPN and VXLAN. VXLAN (Virtual Extensible Local Area Network) is a Layer 2 overlay technology over a Layer 3 underlay infrastructure. And EVPN (Ethernet VPN) is an overlay control plane technology for VXLAN and provides virtual connectivity between different Layer 2/3 domains over an IP or MPLS network.
EVPN-VXLAN can facilitate large enterprises to simplify and optimize their data center or campus networks, creating more agile, secure and scalable Layer 2/3 network connectivity.
Why EVPN-VXLAN?
A large number of applications run in different fields, including cloud, data center, campus, or branch. In the past, applications were designed to live in the same Layer 2 domain, which causes lots of problems.
The EVPN-VXLAN framework runs Layer 3 virtual networks on top of Layer 2 physical networks, called overlays. Overlays offer layers of abstraction on top of the physical networks, allowing newer applications to run over older infrastructure. And Virtualization provides older applications with their virtual networks, enabling them to connect to Layer 2 networks. As a result, EVPN-VXLAN can help data centers manage and protect workloads caused by massive applications. It can also provide a range of benefits to enterprise networks as follows.
Better Performance: Latency between network devices is more predictable, especially in spine-leaf architectures.
Easy Network Scalability: An EVPN-VXLAN architecture enables enterprises to add new data center switches without any redesigns of the underlay network.
Enhanced Security: Network segmentation separates and limits traffic flows generated by a large number of device connections in the network, reducing fault domain and improving network reliability.
Flexibility: MAC address mobility makes EVPN-VXLAN deployment flexible and simple. Moreover, EVPN-VXLAN is an open standard technology with great interoperability. For example, it is easy to integrate into existing networks.
EVPN-VXLAN in the Data Center
EVPN-VXLAN addresses many challenges faced by network operators that are building data centers to deliver cloud and virtualization services. Therefore, IP fabric architecture with EVPN-VXLAN overlay is widely used in modern data centers.
The IP fabric collapses traditional network layers into a two-tier spine-and-leaf architecture, as shown in the diagram below. In EVPN-VXLAN network configurations, spine or leaf devices can function as VXLAN gateways at Layer 2, Layer 3, or both. The implementation of EVPN provides the flexibility to do routing at the leaf or spine or both, depending on the situation. The highly interconnected Layer 3 network provides high resiliency and low latency in the network and can be easily scaled horizontally as needed.
The EVPN-VXLAN overlay sits on top of the IP fabric and can extend Layer 2 connectivity between different data centers, improving the performance of delivering application traffic to end users and for disaster recovery.

Implementing EVPN-VXLAN for Data Centers
The overall architecture of cloud data center integrates business/application systems, cloud operating system platforms, SDN network controllers, network devices and computing storage devices to form a complete cloud data center solution to achieve unified business resource co-scheduling and orchestration.A VXLAN solution with EVPN control plane is preferred in data center interconnect (DCI). There are four options to deploy EVPN-VXLAN for data centers.
Layer 3 VPN-MPLS
Multiple data centers can be connected in the WAN by customer edge (CE) routers. A Layer 3 VPN MPLS network is built between these routers. To configure MPLS Layer 3 VPNs, routers must support MPLS forwarding and Forwarding Information Base (FIB). Data center switches control the VXLAN tunnels. This option is relatively simple to implement and does not require changing your WAN.
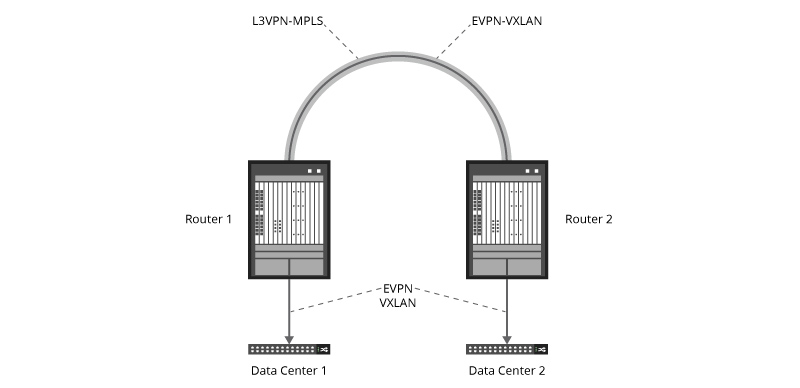
EVPN-MPLS
The second option is to use edge routers or switches to connect multiple data centers in the WAN, building an EVPN-MPLS network between them. This option is more complicated than the previous one, requiring changes to your WAN. And you must change your LAN architecture to natively support EVPN. EVPN stitching is also needed, which refers to configuring two EVPN instances on each of DC Gateway devices and connecting them using Logical Tunnel interfaces.

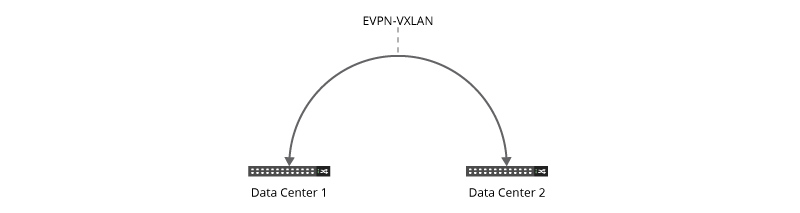
EVPN-VXLAN over the Internet
You can also establish an EVPN-VXLAN tunnel on the IP network between two branch locations, where user-side packets will be encapsulated and forwarded through the tunnel. In this case, neither the traditional WAN nor MPLS is required for implementation, and EVPN is used throughout the Internet or an IP tunnel.

Layer 3 VPN-MPLS Direct Connection
Without a branch router or a peer router, you can simply connect data centers directly. It's as easy to implement as the first option. This implementation does not require either a traditional WAN or MPLS, but typically requires a dark fiber connection. And EVPN is again used throughout.
FS Cloud Data Center VxLAN network solution
FS Cloud data center VxLAN network solution is suitable for operator IDC hosting, finance, education, government and other industries. This solution correspondingly uses VxLAN and BGP EVPN technology to build tenant/service network, that is, Overlay network. It supports different tenants and services to physically share network resources, logically realizes secure isolation and on-demand interconnection, and fully improves the utilization and scalability of the network. In the overall architecture of cloud data center, it integrates business/application systems, cloud operating system platforms, SDN network controllers, network devices and computing storage devices to form a complete cloud data center solution to achieve unified business resource co-scheduling and orchestration.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024














