Deep Comparison Between Server CPU and GPU
As we all know, both CPU and GPU are important components to support server performance, but many people are confused whether their equipment needs CPU or GPU? Although the two server processors are very different, they also have a certain collaboration. Today let's explore the differences between server CPU and GPU.
What Are the Main Differences Between CPU and GPU?
Comprising millions of transistors, the CPU is an integral part of modern systems as it executes the commands and processes required by computers, servers, and operating systems. CPU is suitable for a wide range of workloads, especially those that require low latency and performance per kernel. Any dedicated server will be equipped with one, two, or four CPUs to perform the basic processing of the operating system. As a powerful execution engine, the main working principle of the CPU is to focus a relatively small number of kernels on a single task to process.
Different from server CPU, GPU is a processor composed of smaller, more specialized kernels that can simultaneously process a task across multiple kernels, providing servers with powerful image processing and parallel processing performance. GPU may have lower clock speeds than modern CPU, but with many dense kernels on the chip. It is one of the most obvious differences between CPU and GPU. Originally, GPU was developed for games, and now its functions are more widely used in other fields, such as AI, high-performance servers, etc.
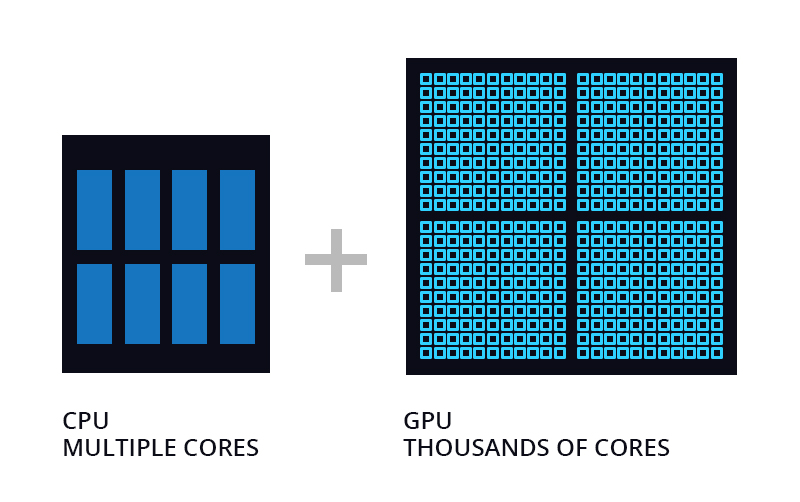
The CPU has fewer logical operation units and a larger proportion of the controller; the GPU has small but many logical operation units, simple controller functions, and less cache. Although the GPU is weaker than the CPU in the processing performance of a single computing unit, a large number of computing units can work at the same time, and its performance is better than that of the CPU when faced with high-density computing. In short, the CPU is good at coordinating the overall complex operations, while the GPU is good at performing simple operations on big data.
Comparison of Server CPU and GPU Applications
Server CPU and GPU have different processing capabilities, and so do the breadth and depth of application. Although GPU has a more extensive application than CPU, we cannot precisely compare which one is better. In fact, at some point, they can work together.
Does Server GPU Work with CPU?
The collaboration of CPU and GPU can increase data throughput and concurrent computation within an application. They work together on the principle that the main program runs on the CPU, while the GPU complements the CPU architecture by allowing repetitive computations within the application to run concurrently. To make an analogy, the CPU is like the task manager of the entire system, coordinating the integral computing range, while the GPU performs finer professional tasks. Compared to CPU, GPU can take advantage of parallel computing performance to do more work in the same amount of time. Servers equipped with both CPU and GPU have higher computing performance and data throughput, which can effectively improve data processing efficiency.

Is GPU More Important Than CPU in a Server?
To understand the importance of CPU and GPU, we must first know their respective application characteristics. A GPU server refers to a server equipped with a graphics card that can run thousands of parallel threads simultaneously. More and more high-performance servers equipped with GPU are emerging in data centers to adapt better to the progress of Internet networks, which greatly reflects the advantages of GPU in multiple processing performances. It has improved the efficiency of data transmission and has a higher return on investment for enterprises.
Compared with the improved performance that server GPU brings, the CPU is also important as a necessary server component. Whether it is a high-performance server, an ordinary server, or a computer, the CPU is indispensable. Server CPU can perform complex tasks while coordinating the overall system. Generally, database queries and data processing are also controlled by it.
Why Not the GPU Run the Operating System Independently?
The GPU has some limitations on the operating system. One of the main limitations is that all the kernels in the GPU only process the same operation at the same time, called SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data). So if you were to do 1,000 similar computing, such as cracking a password hash, the GPU could divide each instruction into different threads to compute in its kernels. However, it is much slower if the CPU and graphics card are used for kernel operations, such as writing files to disk, opening new index pointers, controlling system state, etc.
Compared to CPU, GPU has more latency for operations because of their slower speed due to their more memory computing. And the CPU's transfer and reaction time are shorter for the design of a single fast instruction. To make the same line as an analogy, driving is a single command fast, and subway or bus is a single command with multiple data because the subway and bus have strong capacity and can handle a large amount of demand at a time point. So GPU is tuned to a certain extent in terms of bandwidth, which is another reason why it is suitable for massively parallel processing.
Summary
Both CPU and GPU are critical computing engines for data center servers, referring to chip-based microprocessors in servers or computers. What CPU and GPU both have in common is that they work for a data process, but they still have different architectures and built-in purposes. The CPU is single-instruction fast, and the GPU is single-instruction multi-threading, which also determines the different application scenarios between them. Servers cannot work without CPU, while GPU is used in high-performance servers in data centers and more high-density data processing applications.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024














