Explore Different Security Camera Types: Find Your Ideal Surveillance Solution
From indoor to outdoor, wired to wireless, and analog to network security cameras, understanding these distinctions is crucial when choosing the right surveillance solution. This article is your guide to navigating different types of security cameras, providing insights into their installation locations, wiring methods, transmission modes, physical designs, and functional features.
Click on the following title to jump to the related chapter.
Security Camera Types by Locations
Security Camera Types by Wiring Methods
Security Camera Types by Transmission Methods
Security Camera Types by Appearances
Security Camera Types by Functions
Security Camera Types by Locations
Selecting the right security camera starts with knowing where it will be placed. Indoor and outdoor security cameras each serve specific roles in a surveillance system.
Indoor Security Camera
Indoor cameras are crafted to discreetly monitor the interior of your home or office. These compact devices, such as pet cameras and general home security cameras, can be strategically placed to capture various areas within indoor spaces. Their unobtrusive design makes them ideal for maintaining a watchful eye without disrupting the aesthetics of your living or working environment.

Figure 1: Indoor Pet Security Camera
Outdoor Security Camera
Outdoor cameras, on the other hand, are engineered to withstand the challenges posed by external elements. From rain and snow to varying temperatures, these cameras, including video doorbells, floodlight cameras, and weatherproof security cameras, provide robust surveillance for your exterior spaces. The versatility of outdoor cameras extends to monitoring front and back yards, entry points, and other outdoor areas crucial for comprehensive security coverage.

Figure 2: Outdoor Security Camera
Security Camera Types by Wiring Methods
Once you've determined where your security cameras will be placed, the next crucial consideration is the wiring method. The choice between wired and wireless security camera systems will influence not only the installation process but also the long-term maintenance and scalability of your system.
Wired Security Camera
Wired security cameras, known for their reliable connection, use physical cables like coaxial or Ethernet for transmission and are a staple in settings that require unwavering surveillance, such as financial institutions and government buildings. While cable management might be a consideration with wired setups, the introduction of PoE Kits streamlines the process. These kits combine PoE cameras and a Network Video Recorder (NVR) into a seamless package, channeling both power and data through a single cable and offering a straightforward solution for businesses to establish a robust security system with ease, particularly in office and retail environments.

Figure 3: Wired PoE Security Camera
Wireless Security Camera
Wireless security cameras offer greater installation flexibility and a cleaner aesthetic, as they typically require fewer cables and can connect to your network via Wi-Fi or other wireless technologies. The absence of extensive wiring allows for easier relocation and adjustments. However, it's important to consider that they may be more susceptible to interference and often depend on the strength of the wireless signal or battery life for power.
To learn more: Comparison Between Wired vs Wireless Security Cameras.
Security Camera Types by Transmission Methods
After deciding on the wiring approach for your security cameras—be it wired or wireless—the next key decision involves the transmission method that best suits your overall system requirements. The two primary categories to consider are IP and analog cameras, each with distinct methods of transmitting video signals.

Figure 4 : IP Camera VS Analog Camera
IP Security Camera
IP cameras are advanced surveillance devices that use a network to transmit high-definition video. They can connect with Ethernet for PoE or wirelessly via Wi-Fi. Their benefits include transmitting high-resolution footage and advanced features like remote zoom, ideal for detailed monitoring in retail supermarkets, hotels, amusement parks, and so on.
Analog Security Camera
Analog cameras, often more cost-effective, send video via coaxial cables to DVRs, converting signals for storage and viewing. They suit upgrades of older systems with less need for high-resolution or advanced functions.
For detailed information: IP Cameras vs Analog Cameras, What Are the Differences?
Security Camera Types by Appearances
Security cameras come in various designs, each suited to specific surveillance needs. They can be categorized by appearance into dome, bullet, turret, fisheye, and PTZ cameras. Dome cameras are named for their dome shape, bullet cameras with cylinder-shaped appearance look like bullet shells, turret cameras are with turret style 3-axis construction, and the image from a fisheye camera is hemispherical or wide panoramic, just like the effect of a fisheye and that's how it gets the name. Additionally, PTZ cameras, which stand for pan, tilt, and zoom, are versatile devices that can remotely change direction and focus. We will delve into the specifics of PTZ cameras and their applications in a later section.

Figure 5: Security Camera Types Classified by Appearances
Each of these types of surveillance cameras has a distinct appearance and features and is best suited for different security needs (as the table below).
| Dome Camera | Bullet Camera | Turret Camera | Fisheye Camera | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance |
Dome shape Small size |
Bullet shell shape Highly visible and can easily be damaged |
Sliced sphere shape Small size |
Flat round shape Small size |
| Visual range | Small lens and range | Bigger lens with a wider range | Small lens and range | Ultra-wide range |
| Indoor use | More discreet and less distracting | More visible and easier to vandalize | More discreet and less distracting | More discreet and less distracting |
| Outdoor use |
High concealment Condensation and IR Bounce back |
Wider range Visible deterrent Prone to wildlife nesting |
Clear image No IR Bounce Easy to be damaged |
Clear panoramic image Vandal resistant |
| Installation | Professional installation | Easy installation | Easy installation and adjustment | Easy installation and adjustment |
To learn more: Dome vs Bullet Camera, Turret vs Fisheye Camera: How to Choose?
Security Camera Types by Functions
As security cameras are applied in various environments, different problems and requirements are coming up. To deal with the problems and needs, different types of security cameras are offered: night vision security cameras are designed to get clear images even in complete darkness, WDR IP cameras are invented to deal with overexposure issues, PTZ IP cameras with zoom capability are used to offer a broader field of view with no blind spots, etc. Keep reading to learn more about these functional security cameras.
Night Vision Security Camera
Night vision security cameras are equipped with built-in infrared (IR) LEDs (when looking at the camera lens, you will find them set inside around the lens), and an IR cut filter, which is used to detect daylight and to block out the light falling on the image sensor during the day to keep color in daytime looking accurate.
As night falls, these cameras automatically transition to infrared mode, ensuring they can continue to monitor effectively, even in complete darkness. While most outdoor night vision security cameras capture footage in black and white, advancements in technology now allow some models to provide color night vision, enhancing the detail and clarity of nighttime recordings.
Night vision cameras are widely used in scenarios that require vigilant eyes at all times. From the perimeter of large enterprises and public spaces to the more personal confines of hotel corridors and residential driveways, these cameras ensure that clarity isn't compromised when illumination is scarce.

Figure 6: Night Vision Security Camera
WDR IP Camera
Wide Dynamic Range (WDR) technology compensates for problems with exposure to light. It enables the camera to capture details clearly in both the poorly and strongly illuminated areas of the video. This dynamic treatment of light notably improves the image quality of security cameras under high-contrast lighting conditions where there are both dim and bright areas in the field of view.

Figure 7: WDR Security Camera
WDR technology in IP cameras allows them to capture detailed features by appropriately exposing both the darkest and brightest parts of the entire scene. WDR IP cameras can provide much more concrete images for the identification of people or vehicle license plates, which makes them extremely important for video surveillance systems. Therefore, WDR IP cameras are particularly recommended for building entrances, ATMs, and transportation facilities, as well as near windows or similar areas.
To learn more: Wide Dynamic Range (WDR) in IP Cameras
PTZ IP Camera
PTZ IP camera is equipped with pan, tilt, and zoom functionality controlled by a remote operator using monitoring software or a joystick. You can also use camera management software to set up guard tours so that the security cameras will automatically move to monitor pre-set locations on a schedule. To pan horizontally, tilt vertically & diagonally, and zoom in on a subject, the PTZ IP camera can enhance the image quality without digital pixelation and allows security staff to respond quickly to events they spot with the surveillance camera system.
With the advantages of a large field of view, auto-tracking, remote control, and zoom capability, PTZ IP cameras are commonly applied in guard stations, supermarkets, airports, large outdoor areas, and so on.
Dual-Lens Camera
For enhanced surveillance that doesn't miss a beat, dual-lens cameras are at the forefront of innovation in security technology. As the name suggests, dual-lens cameras incorporate two lenses within a single camera unit. The primary advantage of dual-lens cameras lies in their ability to provide a broader range of information. These cameras can simultaneously capture different perspectives or focus on specific areas of interest. For example, one lens may offer a wide-angle view of the surroundings, while the other zooms in for detailed monitoring. This dual-lens configuration allows for more versatile surveillance options and is particularly useful in scenarios where comprehensive coverage is essential.
Deep Learning Camera
Deep learning is a form of machine learning that can comb through a massive amount of data, recognize patterns, and learn from those patterns. For example, we want to teach security cameras to recognize specific objects. We can programmatically input the size, shape, speed of the objects, and the information of the different components of each object so that the camera can recognize the relevant features. Through this data, the machine learns how to differentiate between the types of movement and decides whether to ignore it.
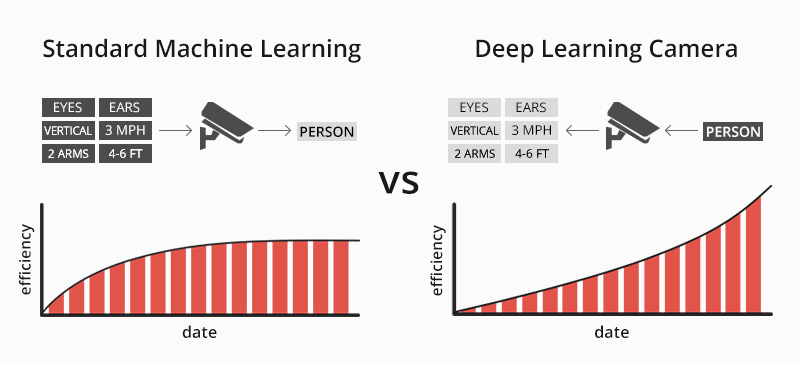
Figure 8: Standard Machine Learning vs Deep Learning Camera
By learning different object classifications, such as a human, animal, vehicle, etc., deep learning cameras can automatically recognize familiar faces, so as to quickly identify people and count the numbers remotely, and realize intelligent alarms in advance. For this reason, face capture cameras are suitable for shops, schools, meeting rooms, and outdoor events.
Thermal Security Camera
Thermal security cameras work by detecting and measuring infrared radiation (heat signatures and patterns) emanating from objects and then constructing images from the differences in their temperatures. As thermal surveillance cameras don't rely on light to get imagery, and atmospheric events like rain, fog, or smoke will not affect their ability to see detailed visibility, they are embraced as ideal “people detectors”.
When properly equipped, they can automatically “catch” intruders attempting to breach outdoor perimeters with high reliability even in an unpredictable outdoor environment. Thermal security cameras support human body temperature screening and face detection with abnormal temperature alarms, ideal for military and commercial vessels, medical facilities, and home and building inspections.

Figure 9: Image of Thermal Security Camera
Conclusion
Understanding different types of security cameras simplifies the decision-making process. Whether you require the flexibility of independent wireless cameras, the robustness of wired solutions, or the advanced features of PTZ cameras, there is an option tailored for every need. If you've found this guide useful, feel free to share this information to empower others to make informed choices for their security needs. Stay informed, stay secure!
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024













