SONET vs. SDH vs. DWDM: Which Technology Supreme?
When compared with traditional SONET or SDH, the next generation of DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is seen as a simple architecture with high scalability, capacity add/drop, multiple ring terminations, multi-services, and multiple fabrics. Then, on comparison of SONET vs SDH vs DWDM, what are their differences exactly? and which technology supreme?
SONET/SDH Basics
What Is SONET/SDH?
The Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) is a standardized protocol facilitating digital communication between senders and receivers. Operating over optical fibers, SONET enables the efficient transmission of vast amounts of data across long distances. A key benefit of SONET is its capability to concurrently transmit multiple data streams, leveraging the power of optical fibers. SONET is standardized by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and it is used in the North American Region.
Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) is an advanced and international version of SONET. SDH is defined as a multiplex technology that is mainly utilized in telecommunication. This advancement has facilitated the establishment of an independent transmission network, free from vendor dependencies, with sophisticated signal structures and notable features. Consequently, the adoption of new network technologies and devices becomes necessary, demanding substantial power to support their operations.
SONET vs SDH
SONET/SDH is the dominant technology deployed in most metro and long distance networks. It refers to a group of fiber optic transmission rates that can transport digital signals with different capacities. The differences between SONET and SDH are below:
-
1. SONET is developed by ANSI (American National Standards Institute) and is primarily utilized in the United States. SDH was created by ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standardization Sector) and is utilized worldwide.
-
2. The basic unit of SDH is synchronous transmission module level-1 (STM-1). The basic unit of SONET is Optical Carrier level-1 (OC-1).
-
3. SONET has 27 bytes of total transport overheads, while SDH has 81 bytes.
-
4. SONET offers lower transmission rates compared to SDH due to the absence of high-order multiplexing for signal transfer.
-
5. SONET can only transmit data synchronously. SDH can only transmit data both synchronously and asynchronously.
DWDM Basics
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a premier technology for increasing bandwidth over existing fiber infrastructure by creating multiple "virtual fibers" through the transmission of different wavelengths of light over a single physical fiber. Initially adopted by long-distance carriers to reduce costs associated with amplification, dispersion compensation, and regeneration in regional and national SONET networks, DWDM has since gained popularity in metro networks due to fiber exhaustion and increasing traffic volumes.
DWDM operates within the 1530 to 1565 nm range, known as the C-band, which aligns with the low-loss window of optical fiber and is compatible with Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFA). The ITU-T standard specifies a grid of allowable wavelengths centered at 193.1 THz (1553.3 nm) with channels spaced at multiples of 25 GHz (0.2 nm). Commercial DWDM systems typically feature channels at 2.5 Gbps, 10 Gbps, and 40 Gbps, with higher bit rates requiring improved signal-to-noise ratios, closer amplifier spacing, and higher amplification, often using two DWDM optical amplifier in series. A standard 64-channel DWDM system at 10 Gbps can reach up to 1,500 km with amplifier spacing around 100 km. Advanced systems can extend the range up to 4,500 km but at a significantly higher cost.
FS DWDM Products and Solutions
If you are looking to establish a DWDM network, FS offers a comprehensive range of high-quality and cost-effective products tailored to meet your needs. Our product lineup includes DWDM Mux/Demux , DWDM optical modules , DWDM EDFA, and DWDM OADM/ROADM. Each product is designed to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Furthermore, FS is committed to providing personalized service and can customize highly efficient DWDM solutions to suit your specific requirements. Whether you need to enhance your current network capacity or deploy a new DWDM infrastructure, our team of experts will work closely with you to deliver the best solutions that maximize your benefits and ensure seamless, high-speed data transmission.
SONET/SDH vs DWDM: Which One Is Better?
The main differences between SDH/SONET and DWDM are listed below:
| Features | SONET/SDH | DWDM |
|---|---|---|
|
Multiplexing
|
Fixed and rigid multiplexing hierarchy and payload structure | Variable and flexible wavelength allocation and payload capacity |
|
Bandwidth Utilization
and Spectral Efficiency
|
Lower bandwidth utilization and spectral efficiency | Higher bandwidth utilization and spectral efficiency |
|
Overhead and Complexity
|
Higher overhead and complexity | Lower overhead and complexity |
|
Number of Topologies
|
For the same traffic, the more number of topological structures are required. | For the same traffic, the less number of topological structures are required. |
|
Cost
|
Cost less in comparison to DWDM | Relatively higher costs |
|
Fiber Requirements
|
More optical fibers required | Fewer optical fibers required |
|
Application
|
Perfect choice when the design requires under 4-10 OC-192 rings, usually for the past network structure | Perfect choice when the design requires over 10 OC-192 rings, better for the future network building |
The need of SONET granularity is due to the presence of low-speed service demands for example DS1/DS3 and the insufficient sub-wavelength grooming within the DWDM platforms. DWDM has a goal to carry the same traffic in as few topological structures (e.g, rings) as possible. DWDM does this at the expense of allowing some visitors to traverse longer distances than it does in SONET. For any simple example, the very best SONET design may generate a bunch of topologically different OC-48 and OC-192 rings, while the most economic DWDM transport network may consist of just a single DWDM ring.
Traditionally, Internet traffic runs on IP, which rides on ATM and SONET/SDH, or IP over SDH, then to an optical layer (as shown in the figure below). The misconception that IP rides on ATM/SDH arises from the need to combine small IP traffic with other services for cost-effective delivery. However, the concept of IP over DWDM supports voice, video, and data traffic, dedicating the remainder to high-speed data traffic. Unlike SDH, which is a time-division multiplexing technology primarily for traditional voice services, DWDM uses different wavelengths to transmit multiple signals simultaneously over the same optical fiber. This difference between SDH and DWDM highlights DWDM's flexibility and efficiency in handling large volumes of data. Eliminating layers like SONET/ATM will ease the task of network management and be cost-effective.
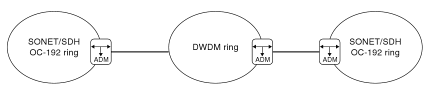
Figure 1.Internet Traffic on SONET/SDH and DWDM
For application, SDH primarily serves as a reliable and synchronized transport mechanism for voice and data traffic in backbone networks, prioritizing interoperability. It is well-suited for legacy systems and networks that require support for multiple protocols and formats. On the other hand, DWDM is predominantly employed to enhance the bandwidth and capacity of optical fiber networks, emphasizing scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. This difference between SDH and DWDM shows DWDM's suitability for emerging systems and networks that necessitate high-speed and high-volume data transmission capabilities.
SONET for the Past
As expected, the SONET scenarios have a low initial cost. When the traffic volume is low, a SONET architecture is much more economical compared to DWDM architecture. FS’s modeling indicates that when designing a SONET overlay network with OC-3, OC-12, OC-48 and Gigabit Ethernet demands so when the design requires under 4-10 OC-192 rings, a SONET network is a perfect choice.
DWDM for Now and Future
As the traffic volume grows, DWDM will eventually prevail and become the choice of the network technology. Timing of this crossover is responsive to such things as the span distances, pricing and interface density. The differences between demand types mostly are caused by the design efficiency of these two technologies’ interface cards in terms of density and price. FS’s study also shows span distances usually trigger the extra requirement for regenerators, optical amplifiers and DCMs in the routes. Long span distance has a tendency to favor a DWDM architecture because of the efficient utilization of fibers and optical bypass capabilities at intermediate nodes.
Additionally, higher fiber cost and situations in which fiber constraints are enforced will lead to more consideration for DWDM than SONET because DWDM saves a tremendous amount of fiber within the optical network. DWDM systems could be planned for a large number of channels, however, pay-as-you-grow strategy can be used and channels added based on demand in FS. The amplifier distance and overall power budget of the system needs to be calculated for the final quantity of channels right from the start.
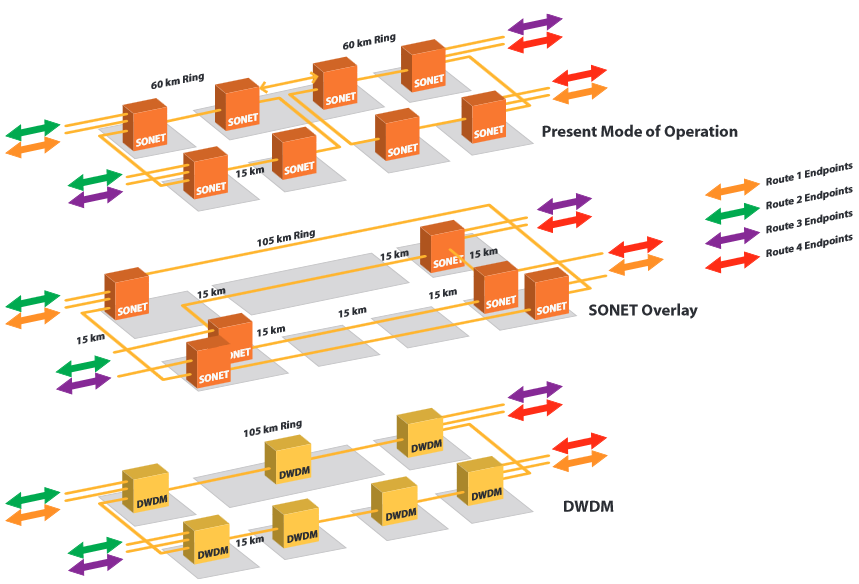
Figure 2.SONET vs DWDM
Conclusion
Different alternatives and their economic impact in designing exactly the same network is definitely an interesting study. SONET point-to-point performs better still. These results might not apply in all situations. However, the implication is the fact that, in large network designs, the most optimized network may not necessarily be a single architecture. One part of the network may adopt rings while another part implements point-to-point. Usually, the core part of the network will justify a DWDM architecture.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024














