Trends in 400G Optical Fiber Cabling for Data Centers
 Data Center has witnessed an increasingly higher bandwidth and speed owing to the massive demand for high-capacity workloads and upgrade of data center infrastructures. Optical fiber cabling, due to its features of high bandwidth, long transmission distance and flexibility, is widely admitted as the main cabling solution in data centers. As large data centers are preparing for the implementation of 400G, 400G optical fiber cabling becomes an inevitable trend.
Data Center has witnessed an increasingly higher bandwidth and speed owing to the massive demand for high-capacity workloads and upgrade of data center infrastructures. Optical fiber cabling, due to its features of high bandwidth, long transmission distance and flexibility, is widely admitted as the main cabling solution in data centers. As large data centers are preparing for the implementation of 400G, 400G optical fiber cabling becomes an inevitable trend.
Drivers for 400G Optical Fiber Cabling in Data Centers
The journey to higher speed in data center is a step-by-step process. The implementation of 400G optical fiber cabling is affected by many factors.
Data Center Upgrade
Data Center today witnessed several generations of speed upgrades, from 10G bps to 100Gbps/200Gbps and 400Gbps. As data centers grow in size and the equipment changes over time, the old cabling system is no longer suitable for the new data center requirement. Optical cables must be able to support transmission for 400G to 400G links or 400G to 100G/200G links, connecting every server and switch.

On the other hand, the old data center system means worse network performance. Especially for data centers with equipment and cabling system working for 4 years or longer, it is suggested to replace the component of the whole system for better long-term performance.
Evolving IEEE and ANSI/TIA Standards
To accommodate the explosive growth of bandwidth, the IEEE802.3 and ANSI/TIA standard working groups have been working to update the wired Ethernet standards, of which the former pushes the boundaries of Ethernet to new applications and the latter redefines the cabling standards.
Back in 2017, the IEEE completed its 802.3bs standard for 400G, which defined the 400G standards covering multimode and single mode optical fiber running from 70m up to10km as shown in the chart below. ANSI/TIA group also develops and updates the cabling standard to support IEEE standards for 400G Ethernet applications. Both the working groups help to standardize the optical fiber cabling system and build optimized cost-effective links for 400G applications.
| IEEE Standard | Fiber Type | Link Length |
|---|---|---|
| 400GBASE-SR16 | MMF | 100m |
| 400GBASE-SR8 | MMF | 100m |
| 400GBASE-DR4 | SMF | 500m |
| 400GBASE-FR8 | SMF | 2km |
| 400GBASE-LR8 | SMF | 10km |
Innovation in Optics Technology
With the increasing need for higher speed and efficiency, optics technology keeps moving towards. 400G IEEE standard calls for the use of both multimode and single mode fiber though single mode fiber is considered to be the main transmission media type in hyperscale data centers for its longer transmission distance. The multimode fiber cable - OM5 is introduced. Unlike the traditional multimode fibers operated at a single wavelength, OM5 is known as wideband multimode fiber to support multiple wavelengths. In addition, PAM4 is another innovation for doubling bit rate and increasing the fiber link capacity. These innovations are accepted by IEEE, ANSI/TIA standards, and MSAs, paving the way for an upgrade to 400G applications.
400G Optical Fiber Cabling Has Arrived: Trends and Characteristics
Driven by need for data center upgrades, the maturity of 400G standards and the development of optics technology, 400G optical fiber cabling is on the rise.
High-Density Fiber Links
Driven by the rapid growth of data in 5G and IoT deployments, the demand for data center capacity is soaring more than ever before, which means the amount of equipment is increasing. Higher bandwidth pushes data center equipment and cabling system to improve efficiency and performance so as to keep data centers competitive. Nowadays fiber backbones in the data centers are using more strands than ever before. High-density optical fiber cabling solutions are required. There are several solutions data center operators can take, for example, breakout fiber assemblies and the cable management tools, helping to eliminate the challenges for 400G high-denstiy fiber cabling deployments in data centers.
New Packaging and Designs
Traditional cable technology of standard ribbon fiber optic cable splices 12 strands in a strip. As more strands are needed for connections within a data center and inter-data center, the key issue lies in how to deploy fiber cabling with an increased number of fibers without increasing the cabling footprint. Some cable OEMs develop rollable-ribbon construction and 200-micron fiber, doubling the number of fibers and keeping the cable size the same as traditional cables.

New cable packaging innovation balances cost and performance, making hyperscale data center cabling available in limited spaces.
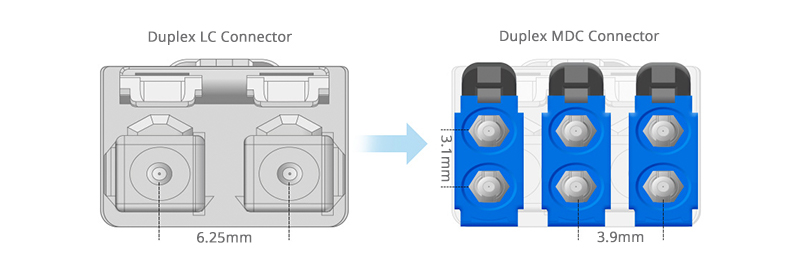
Small Form Factor Connectors
The 400G market introduces a new connector category which is called "very small form factor connectors" (VSFFC), such as SN and MDC connectors. Taking duplex MDC as an example, it offers 3 times the fiber cabling density of duplex LC connectors. The combination of MDC to LC SMF cable and MDC fiber adapter enables 400G to 400G interconnect solution for data center backbone cabling.
Deploying a high-density cabling solution is an inevitable trend, while these small form factor connectors serve as a futureproof and cost-effective platform. We can expect that with the rising growth of data in data centers, optical fiber cabling with small form factor connectors will improve data center efficiency and scalability to a great extent.
Road to 400G and Beyond
400Gbps has become a reality, although it currently occupies a small market and is not widely deployed in the industry, massive adoption of 400Gbps in data centers is on the rise over the coming years.
As technological innovation develops, the pressure that hyperscale data centers face will not diminish but require data center operators to take future-proofed cabling solutions to cope with the growing needs. There are manufacturers developing cabling solutions supporting data speeds up to 800Gbps and even 1.6Tbps. The era of 800Gbps and 1.6Tbps will not be far away when 400Gbps is selected by customers from different industries to address network challenges.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024













