What Is Armored Fiber Cable?
As is known, armored fiber cable can provide extra protection for fiber optic cable without sacrificing flexibility or functionality within fiber networks, featuring more robust and reliable when encountered with rodents, moisture, and other issues that may cause damage. The armored fiber cable is now optimal for campus & building backbones, data centers, and industrial applications. This article will lead you to know this armored optical cable.
Armored Fiber Cable Basics
What is an Armored Fiber Cable
Armored fiber cable is a type of fiber cable with an enhanced protective layer or metal jacket. It is renowned for its durability and resistance to external damage, making it ideal for harsh environments and applications requiring high physical protection. This cable boasts excellent environmental adaptability, resisting vibrations, extreme temperatures, and moisture. Its metal jacket also provides enhanced fire resistance and safety.
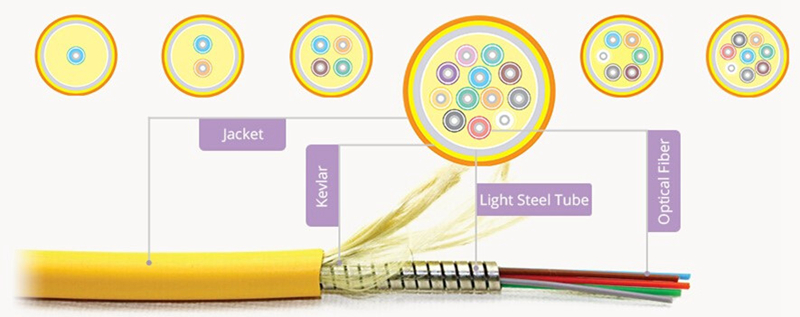
What is the Structure of Armored Fiber Cables?
Optic Fiber: The core component of the cable, which is the central component of the cable and consists of one or more optical fibers that transmit data signals in the form of optical pulses, which are responsible for transmitting optical signals.
Light Steel Tube: The light steel tube between the optic fibers and the outer jacket offers better protection to the fibers in the center. This layer acts as armor to protect the inner fibers from physical damage. The steel tube shields the fibers from compression, bending, wear, and potential rodent bites.
Kevlar: The Kevlar is placed inside the outer jacket to cover the steel tube. This is a strength member used to provide additional support to the cable. Kevlar fibers enhance the tensile strength of the cable, making it more resistant to physical stresses such as pulling and stretching.
Outer Jacket: The outermost layer of the fiber cable protects against environmental factors such as moisture, ultraviolet radiation, and chemicals. Materials commonly used for the jacket include polyethylene (PE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
What are the Benefits of Armored Fiber Cables?
Durability: Armored fiber cables have excellent resistance to mechanical damage, waterproofing, moisture resistance, and wear resistance, significantly improving their service life in complex and extreme environments, and effectively reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Security: Armored fiber cables effectively prevent rodent invasion and electromagnetic interference, and have strong physical protection capabilities to ensure the reliability of communication networks and the integrity of data transmission, providing high standards of security.
Economical: Armored fiber cables achieve significant cost savings in the long run due to their durability and resistance to damage, which reduces maintenance and replacement costs, simplifies the installation process, and improves physical protection.
Armored Fiber Cable vs Unarmored Fiber Cable
Compared with standard fiber optic cables, armored fiber optic cables enhance protection by using internal stainless steel pipes, providing greater compression and tensile resistance. Standard fiber optic cables usually consist of tightly buffered fibers, aramid yarns, and jackets, while armored cables add a layer of stainless steel armor between the tightly buffered fibers and aramid yarns. This reinforcement significantly improves the cable's ability to withstand lateral pressure without affecting its optical performance and preventing mechanical damage. In addition, armored cables also have the function of impact resistance and preventing rodent bites, making them suitable for use in harsh environments.

Armored Fiber Cable Types
The armored fiber cables can be classified into several types in terms of different classifications, which include the type of metal tube within the cable, the installation methods of the cable, and the specific applications.
Classification According to Metal Tube
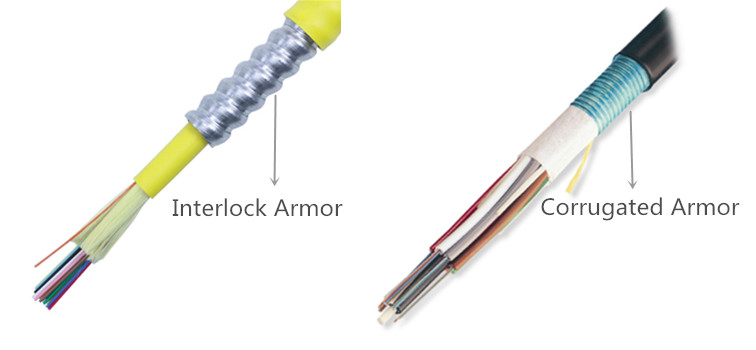
Armored fiber optic cable can be divided into two types according to the metal tube: interlock armored fiber cable and corrugated armored cable. Interlocking armor is aluminum armor that is helically wrapped around the cable and found in indoor and outdoor cables, which offers ruggedness and superior crush resistance. Corrugated armor is coated steel tape folded around the cable longitudinally, which can be found in outdoor cables and offers extra mechanical and rodent protection. Both armored fiber cables enable installation in the most hazardous areas, including environments with excessive dust, oil, gas, moisture, or even damage-causing rodents.
Classification According to the Installation Method
As mentioned before, there is a strong metal armored tube inside the armored fiber cable. Therefore, the termination of the armored fiber cable is more difficult than that of standard fiber optic cables. Field-terminated armored fiber cables have better performances in some outdoor applications, while pre-terminated ones are adopted by many installers for indoor applications considering quality transmission and time-saving factors.
Furthermore, the pre-terminated armored fiber cables provided by the market are mainly armored fiber patch cable and armored fiber trunk cable: the former is stronger and more flexible than the traditional fiber patch cable, while the latter is a length of armored fiber cable with several legs on each end terminated with fiber optic connectors.

Classification According to Application
Armored fiber cable can be used for indoor and outside plant (OSP) applications. According to different installation environments, tight-buffered armored cable and loose-buffered armored cable are generally adopted: Both loose-buffered and tight-buffered armored fiber cable can fit indoor and outdoor applications, but loose-buffered ones are more often used in outdoor applications.
Indoor Armored Fiber Cable: The armored cable used for indoor applications often consists of tight-buffered or loose-buffered with strength members and an inner jacket. The inner jacket is commonly surrounded by a spirally-wrapped interlocking metal tap armor. Typical indoor armored fiber cable types include GJFJV, GJFJZY, GJFJBV, GJFJBZY, GJFDBV, and GJFDBZY. With the fast development of fiber optic communication technology and the trend of FTTX, the demand for installing indoor fiber optic cables between and inside buildings is fast-growing.
Outdoor Armored Fiber Cable: Armored cable for outdoors is designed to ensure operation safety in complicated outdoor environments, and most of them are loose buffer designs. Light armor and heavy armor are the two versions of outdoor armored fiber optic cable. The lightly armored cable possesses a protective plastic jacket with the same durability and longevity as a stainless steel cable but at a lighter weight, which is suitable for a myriad of applications from interconnects to industrial and semi-harsh environment conditions. The heavily armored cable is wrapped in a wire circle that can protect the fibers from gnawing animals and damages that occur during direct burial installations, which is applied for the river bed and ocean floor.
Armored Fiber Cable Installation Guide
Armored fiber optic cable caters to both the rigorous environment of the outdoor but also can be routed indoors. Despite the numerous benefits armored fiber cable retains, it also yields some inconvenience to bond and ground the cable. To handle the problem that may occur during the installation, wisely perform the following steps.
-
Bend Cable—Bend the armored cable about 10 inches from its end and squeeze with your hand until the coils of the armor come apart. If you can't do this by hand, use pliers, or employ another cutting method.
-
Twist Cable—Firmly grip the armored cable on each side of the cut and twist until the split-apart armor coil pops out, away from the wires. Use two pairs of pliers if you can't do this by hand.
-
Cut Exposed Coil—Using side cutters, cut the exposed coil of sheathing. You may have to grab the coil with the side cutters and work it back and forth to open and make the cut.
-
Cut the Wires—If you are cutting a piece to length, slide back the sheathing and cut through the wires. Otherwise, slide the waste piece off and throw it away.
-
Remove Excess—Cut off any sharp points of sheathing using side cutters. Remove the paper wrapping and any thin plastic strips.
Summary
Armored fiber cable presents a premium solution to secure the network by protecting fiber links, which is specified as the primary backbone due to its distinct advantages for space efficiency, lower cost of materials and installation, as well as less risk of downtime and damage.
Related Article: What Kind of Fiber Patch Cord Should I Choose?
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
May 30, 2024















