VPN vs MPLS: What’s the Difference?
 Nowadays, VPN and MPLS are two competing technologies to keep data stored and secure efficiently. But what exactly are they and how do they differ from each other? This post will give a detailed introduction to the difference between VPN and MPLS, and set out how to make a proper decision over VPN vs MPLS.
Nowadays, VPN and MPLS are two competing technologies to keep data stored and secure efficiently. But what exactly are they and how do they differ from each other? This post will give a detailed introduction to the difference between VPN and MPLS, and set out how to make a proper decision over VPN vs MPLS.
VPN vs MPLS: What Is VPN?
VPN, also known as Virtual Private Network, is basically a virtual network within a physical network. It is generally deployed to be high security network tunnel through which data travels in a strongly encrypted form. Thus, any data travelling over a VPN is not visible to the physical network surrounding it. VPN can be created through a various type of encryption, such as IPsec, SSL and TSL. Among them, IPsec is the most widely used.
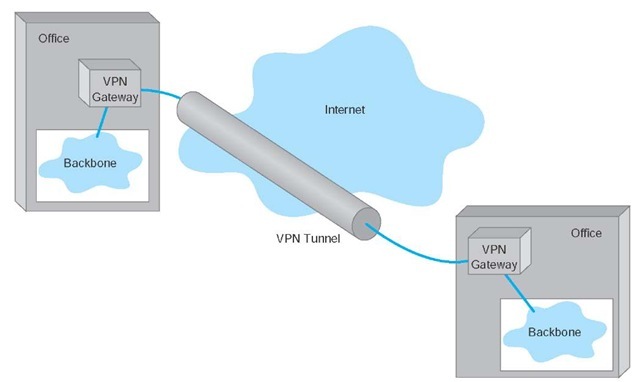
VPN vs MPLS: What Is MPLS?
MPLS is short for Multi-Protocol Label Switching, which is a protocol that uses labels to route packets instead of using IP addresses. It is a technology directs and carries data between network nodes, which means it’s possible to create direct virtual links between different nodes regardless of locations and distances. Unlike VPN, MPLS is a mechanism independent of protocol and data, therefore it can work regardless as to the physical network topology. Due to this flexibility, many suppliers have developed their network switches suited for MPLS platform. For example, FS S5800-48F4S 10GbE switch enables LSR in an MPLS network to exchange label binding information for supporting hop-by-hop forwarding. For more information on this switch, please read FS S5800-48F4S MPLS Switch: the Best Mix of Layer 2 and Layer 3

VPN vs MPLS: What’s the Difference?
VPN and MPLS differ from each other not only in the above mentioned aspects but also at cost, performance, application, etc. To be clear here lists the difference between VPN and MPLS in the following chart:
| Parameters | VPN | MPLS |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Type | Point to Point and Multipoint technology. | Multipoint technology |
| OSI Layer | Works on up to Layer 7 | Works between Layer 2 and Layer 3 |
| Encryption | Use encryption | Do not need encryption |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Traffic Prioritization | Not possible | Possible |
| Platforms Support | Supported on Routers (with relevant security license) and Firewalls | MPLS can be terminated at any layer 3 device such as Router, Firewall, Layer 3 Gigabit Ethernet switch, etc. |
| Multicast Support | Not supported on IPsec VPN. Need to implement GRE over IPsec which incurs additional configuration and overhead | Support multicast traffic |
| Target Customers | Suitable for small to medium sized enterprises | Suitable for large-size enterprises |
| Provisioning and Management | Customer needs to perform configuration and provisioning of VPN setup over IPsec supported box | Service provider is responsible for providing and maintaining MPLS connectivity, which relieves customers from burden of configuring the devices |
| Traffic Control and Routing Decision | Customer has the control over traffic routing | Service provider has more traffic control and its routing |
| Location Limitation | Basic requirement being Internet termination at customer sites from any provider | Limited up to locations where service provider has network laid out or has partnership with another service provider |
| Delay Sensitive and Mission Critical Traffic | Less preferred & reliable for delay sensitive traffic and business critical application | More reliable and provides better user experience considering QoS has been implemented |
| Deployment Time and Network Availability | Easy and fast deployments like SSL/IPsec remote access VPN for remote home user via Internet. | Easy and fast deployments like SSL/IPsec remote access VPN for remote home user via Internet. |
| Cloud Based Services | Wide array of Cloud based services available for customers over Internet using VPN based connectivity | Limited availability of Cloud-based services for customers over MPLS |
VPN vs MPLS FAQs
Is MPLS more secure than VPN?
Actually, VPN can provide a higher degree of security and privacy than MPLS does.
-
MPLS: As a private network with proprietary infrastructure and routing protocols, MPLS is not susceptible to traffic hacking. But once the MPLS equipment is set improperly, users will face data risk. What's more, since the data isn't encrypted in MPLS, if someone enters the network, users' privacy is at risk. At that point, users may experience severe data loss, such as passwards, bank accounts and other sensitive information.
-
VPN: Compared to MPLS, VPN works more effectively in terms of data security. Firstly, VPN usually uses multiple layers of defense to protect users' private information, therefore it is difficult for hackers to enter the network. In addition, unlike MPLS, data in VPNs is encrypted, so even if users suffer a data attack, they are still not vulnerable to data loss or risk, because hackers cannot make sense of the data. What's more, lots of enterprises also provide VPN with extra security features, such as building a kill switch into their VPNs.
Is MPLS Faster Than VPN?
In fact, there is no precise answer to this question. Whether MPLS is faster than VPN depends on the specific settings of networks.
Traditionally, MPLS do enjoy faster speed when it comes to internet connection, because it doesn't use traffic encryption, which is pretty time-saving. Besides, since MPLS uses labels to route packets instead of using IP addresses, it can improve connection speeds to some extent. What's more, being smaller and more inclusive, MPLS can also achieve faster data connection than VPN.
By contrast, VPN will slightly slow down the speed of internet connection, since data has to be encrypted and routed through a virtual server, which is time-consuming. However, VPN can also speed up traffic. For example, using VPN can help users to hide their online activity from the internet service providers (ISPs), thus bypassing traffic throttling.
VPN vs MPLS: Which One to Choose?
VPN and MPLS each has its own pros and cons. So you’d better do a cost–benefit analysis to help you decide before deploying VPN or MPLS network. In fact, choosing VPN or MPLS depends on your business requirements, which can come down to such factors as cost, security, availability, QoS, speed , etc. For example, If your company is running critical, real-time applications across the network (such as voice, video or remote desktop), MPLS is a perfect solution. While VPN is suitable for those who want to save cost and has low request for QoS, speed, etc.
You might be interested in
Email Address

-
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
Mar 16, 2023














